Artificial Intelligence (AI) Explained: Definition, Types, and Applications

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transitioned from a concept in science fiction to a transformative force shaping various facets of our lives. In the current landscape of 2024, AI’s influence continues to expand, permeating industries, revolutionizing businesses, and altering the ways we interact with technology.
Professionals view artificial intelligence as a production element capable of ushering in fresh avenues for growth and transforming workflows across sectors. As an illustration, according to a PWC report, AI is forecasted to potentially add $15.7 trillion to the worldwide economy by 2035. China and the United States stand poised to reap the greatest advantages from the impending surge in AI, jointly accounting for nearly 70% of its global impact.
The tutorial offers a comprehensive insight into Artificial Intelligence (AI), including how it works, advantages and disadvantages, diverse applications, and why it’s a good field to master.
Read more: Top 10 AI and Machine Learning Trends for 2024
What is Artificial Intelligence?
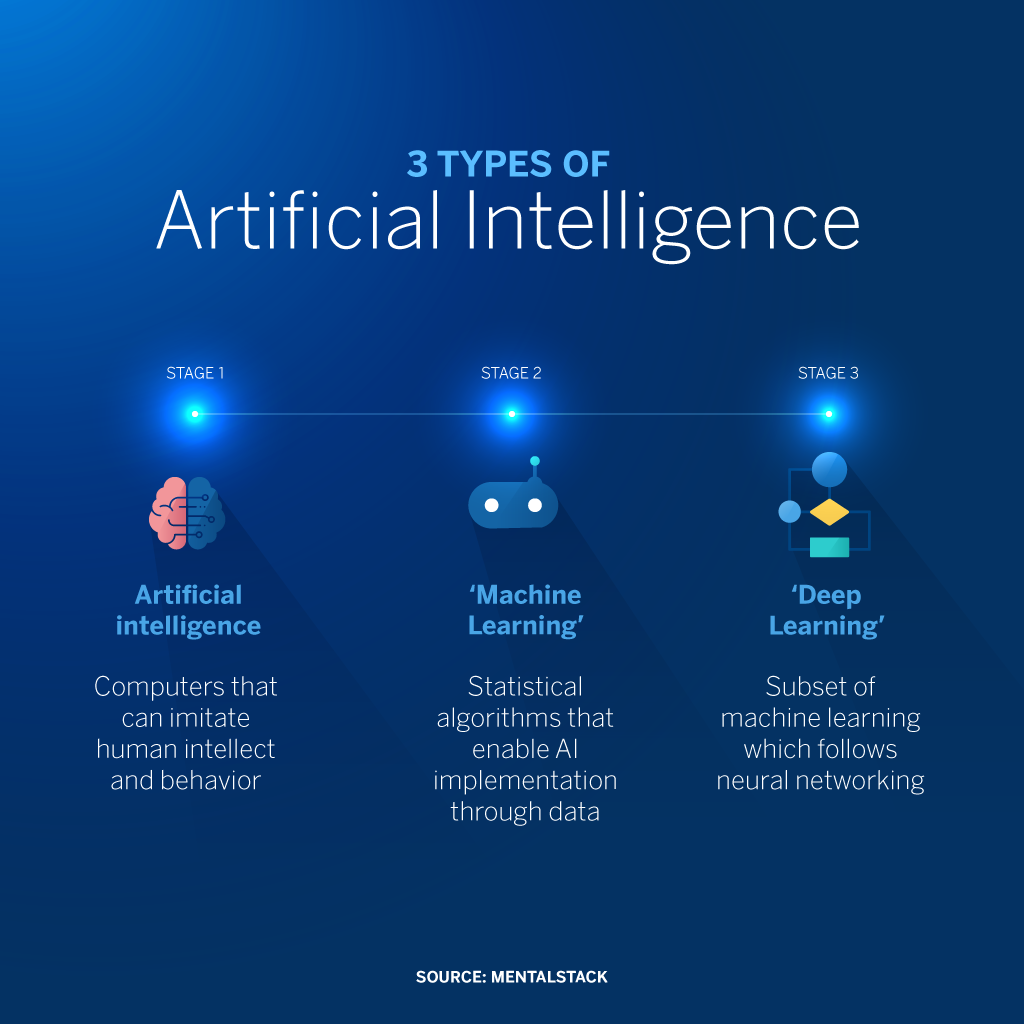
At its core, Artificial Intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to think, learn, and problem-solve like humans. AI systems are designed to mimic cognitive functions such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding. The goal of AI is to develop systems that can analyze data, adapt to new situations, and perform tasks autonomously, mirroring human intelligence and behaviors.
This field encompasses diverse subsets, including Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Computer Vision, and more.
Machine Learning, a prominent branch of AI, enables machines to learn from data patterns and improve their performance without explicit programming. Deep Learning, a subset of ML, involves complex neural networks capable of processing vast amounts of data to make decisions or predictions. Natural Language Processing focuses on enabling machines to understand and generate human language, facilitating advancements in chatbots, language translation, and sentiment analysis.
Deep Learning vs. Machine Learning
Deep Learning and Machine Learning are two subsets of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that differ primarily in their architecture, approach to data, and complexity of tasks they can handle.
1. Machine Learning (ML)
- ML is a broader concept within AI that involves algorithms enabling machines to learn patterns from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. It encompasses various techniques such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
- In supervised learning, models are trained on labeled data, learning to map input to output based on provided examples. It’s commonly used in tasks like classification and regression.
- Unsupervised learning involves algorithms learning patterns and structures from unlabeled data, finding hidden patterns or groupings within the data.
- Reinforcement learning focuses on training agents to make sequences of decisions by rewarding desired behaviors and penalizing undesired ones based on feedback from the environment.
- Machine learning models need handcrafted features to represent data, and their performance may plateau when dealing with complex tasks or large datasets.
2. Deep Learning (DL)
- Deep Learning is a specialized subset of machine learning that employs neural networks with multiple layers (deep neural networks) to process and analyze data. These networks can automatically learn hierarchical representations of data, discovering intricate patterns and features.
- DL models excel in handling large volumes of complex data, such as images, audio, text, and video, without the need for manual feature extraction.
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are a type of DL model particularly well-suited for image recognition and computer vision tasks.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are used for sequential data, such as text or time series, enabling tasks like language translation and speech recognition.
- Deep Learning models are highly effective in tasks like image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous driving.
In essence, while Machine Learning involves various algorithms that learn from data and make predictions or decisions, Deep Learning is a specialized form of ML that uses neural networks with multiple layers to automatically extract hierarchical representations of data, particularly well-suited for complex tasks involving unstructured data like images, audio, or text. Deep Learning has shown remarkable performance in various AI applications, but it requires substantial computational resources and large amounts of data to train complex models effectively.
Weak AI vs. Strong AI
Weak AI and Strong AI are two contrasting concepts within the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that denote varying degrees of intelligence and capabilities in AI systems:
1. Weak AI (Narrow AI)
- Weak AI refers to AI systems that are designed and trained for specific tasks or a limited range of tasks. These systems are specialized and focused on solving particular problems without possessing general intelligence or consciousness.
- They excel in performing predefined tasks and can simulate human-like abilities within a narrow domain. Examples include virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, or chatbots, as well as specific machine learning models for tasks like image recognition or language translation.
- Weak AI systems are proficient in the tasks they are designed for but lack the broad spectrum of cognitive abilities and self-awareness found in human intelligence.
2. Strong AI (General AI or AGI – Artificial General Intelligence)
- Strong AI, on the other hand, refers to AI systems or machines with generalized human cognitive abilities. These systems possess intelligence and consciousness comparable to that of human beings, allowing them to understand, learn, reason, and solve problems across various domains and contexts.
- Strong AI aims to mimic human-like intelligence comprehensively, including the ability to apply knowledge and skills from one domain to another, exhibit self-awareness, and learn in a manner akin to human learning.
- Achieving Strong AI remains an aspirational goal in AI research, as current AI systems are primarily Weak AI and have not achieved true general intelligence or consciousness.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
The classification of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into different types is often based on their capabilities and functionalities. The categorization includes:
1. Purely Reactive AI
These AI systems operate in the present moment and make decisions based solely on current data without any memory or past experiences. They do not have the ability to retain or use historical data for decision-making. For example, in a game of chess, a purely reactive AI evaluates the current board position and makes the best move based on that specific scenario.
2. Limited Memory AI
Unlike purely reactive systems, AI with limited memory retains some past data or experiences to improve decision-making. These systems store a certain amount of historical data to enhance their understanding or predictions. For instance, recommendation systems using limited memory AI consider past user preferences to suggest movies, restaurants, or products.
3. Theory of Mind AI
This hypothetical type of AI remains under development and aims to comprehend human emotions, thoughts, and social interactions. A machine with the theory of mind could understand human intentions, beliefs, and emotions, allowing it to interact more convincingly in social settings. However, this kind of AI is yet to be realized.
4. Self-Aware AI
This category represents an AI system that possesses consciousness, self-awareness, and human-like intelligence. Self-aware AI would not only understand its environment but also recognize its own existence, emotions, and thoughts. Currently, this type of AI remains theoretical and is a subject of philosophical and ethical discussions rather than a realized technological development.
It’s important to note that while the first two types, purely reactive and limited memory AI, are currently in use, theory of mind and self-aware AI remain largely conceptual and theoretical. The latter two types pose significant challenges and raise ethical considerations that extend beyond the realm of technology and delve into philosophical and existential questions about consciousness and the nature of intelligence.
How Does Artificial Intelligence Work?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) works through the use of algorithms and computational models that enable machines to simulate human-like intelligence, learn from data, and perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. The functioning of AI involves several key components and processes:
- Data Collection: AI systems rely on vast amounts of data to learn and make decisions. This data can be structured or unstructured, including text, images, videos, sensor data, or any other form of information relevant to the task.
- Data Preprocessing: Before feeding data into AI models, preprocessing steps are often required to clean, transform, and prepare the data. This involves tasks like normalization, encoding, feature extraction, and handling missing values to ensure the data is suitable for analysis.
- Algorithms and Models: AI algorithms form the core of AI systems, defining how data is processed, analyzed, and used for decision-making. These algorithms can include various approaches such as machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), natural language processing (NLP), and more. Different algorithms are applied based on the nature of the task and the type of data involved.
- Training the Models: In machine learning and deep learning, models are trained using labeled or unlabeled data. During the training phase, the algorithm learns patterns, relationships, and features from the data to make predictions or classifications. This training involves adjusting the model’s parameters iteratively to minimize errors or improve performance.
- Inference or Prediction: Once trained, the AI model is deployed for making predictions, classifications, or generating outputs based on new, unseen data. The model uses the learned patterns to infer or predict outcomes in real-time.
- Feedback Loop and Improvement: AI systems often operate in a feedback loop, continuously learning and improving from new data and feedback. This iterative process of learning from new information allows the AI model to adapt, refine its predictions, and enhance its performance over time.
- Decision-Making and Task Execution: Depending on the AI system’s purpose, it can execute various tasks, such as recommending products, analyzing medical images, translating languages, autonomously driving vehicles, or assisting in decision-making processes.
- Ethical Considerations and Monitoring: As AI systems make decisions and automate tasks, it’s crucial to monitor their behavior, detect biases, ensure ethical use of data, and maintain transparency in decision-making processes. Ethical considerations and responsible AI practices are integral to the development and deployment of AI systems.
AI systems vary in complexity and application, but they all involve the interplay of data, algorithms, learning, and decision-making processes to replicate human-like intelligence and perform tasks efficiently and accurately.
Pros and Cons of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers numerous advantages, but it also comes with certain drawbacks and challenges. Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of AI:
Pros of AI
- Automation and Efficiency: AI enables automation of repetitive tasks, improving efficiency and productivity in various industries. It reduces human effort and time in performing routine activities.
- Improved Decision-Making: AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, leading to better-informed decision-making processes. This aids businesses in forecasting trends, identifying patterns, and making data-driven decisions.
- 24/7 Operations: AI-powered systems can operate continuously without fatigue or breaks, providing round-the-clock services, such as customer support or data processing.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Precision: AI algorithms, particularly in fields like healthcare and manufacturing, can perform tasks with a higher degree of accuracy, reducing errors and improving outcomes.
- Innovation and Creativity: AI fosters innovation by enabling the development of new technologies, products, and services. It can assist in creative tasks like art generation, design, and content creation.
- Personalization and User Experience: AI-driven personalization improves user experiences by tailoring recommendations, content, and services to individual preferences, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
Disadvantages of AI
- High Initial Costs: Implementing AI systems often involves significant initial investments in infrastructure, technology, and talent, making it costly for some businesses to adopt.
- Job Displacement: Automation by AI could lead to job displacement as machines take over tasks traditionally performed by humans, potentially impacting employment in certain industries.
- Lack of Creativity and Empathy: While AI can perform specific tasks efficiently, it lacks human qualities like creativity, intuition, empathy, and emotional understanding.
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns: AI systems rely on large amounts of data, raising concerns about data privacy, security breaches, and misuse of personal information.
- Ethical Issues and Bias: AI systems can inherit biases from the data they are trained on, leading to biased decision-making, perpetuating societal biases, and ethical concerns regarding fairness and transparency.
- Dependency and Reliability: Over-reliance on AI systems without human oversight could pose risks in situations where systems malfunction or make incorrect decisions.
- Lack of Explainability: Some AI models, particularly complex deep learning models, lack transparency in how they arrive at decisions, making it difficult to explain their reasoning.
Understanding these advantages and disadvantages is essential in harnessing the potential of AI while addressing its challenges responsibly. Efforts to mitigate the drawbacks and ethical considerations surrounding AI development and deployment are crucial for its responsible and beneficial integration into society.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is prevalent across various industries, showcasing its capabilities in diverse applications. Here are several applications of AI in action:
Virtual Assistants
AI-powered virtual assistants like Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri, Google Assistant, and Microsoft’s Cortana use natural language processing (NLP) to understand and respond to user queries, manage tasks, and provide information.
Recommendation Systems
Platforms such as Netflix, Amazon, and Spotify use AI algorithms to analyze user preferences and behavior, providing personalized recommendations for movies, products, or music.
Healthcare and Medical Diagnosis
AI assists in medical imaging analysis, aiding in the interpretation of X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans for more accurate diagnoses. Additionally, AI-powered chatbots help in providing initial medical advice and assistance to patients.
Autonomous Vehicles
AI plays a crucial role in self-driving cars and autonomous vehicles. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Uber use AI algorithms for navigation, object detection, and decision-making in autonomous driving systems.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP applications include language translation services like Google Translate, sentiment analysis in social media monitoring tools, chatbots for customer service, and voice recognition systems.
Financial Services
AI is used in fraud detection, risk assessment, algorithmic trading, and personalized financial advice. It helps in analyzing large volumes of financial data quickly and accurately.
Read more: AI in FinTech: 7 Ways AI is Transforming the FinTech Industry
Manufacturing and Robotics
AI-powered robots and automation systems assist in assembly lines, quality control, and warehouse management. Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside humans to perform tasks efficiently.
Gaming
AI is used to create intelligent agents in video games, enabling NPCs (non-player characters) to react to player actions, adapt strategies, and enhance the gaming experience.
E-commerce and Customer Support
AI-driven chatbots facilitate customer service interactions, providing instant support, answering queries, and guiding users through purchasing decisions on e-commerce platforms.
Smart Home Devices
AI-powered smart home devices like smart thermostats, security cameras, and appliances use machine learning algorithms to learn user preferences and adapt their behavior accordingly.
Content Generation and Creativity
AI technologies contribute to content creation, such as writing articles, generating art, composing music, and creating design prototypes.
These examples illustrate the versatility and impact of AI across multiple sectors, showcasing its ability to enhance efficiency, decision-making, and user experiences in various domains. As AI continues to evolve, its applications are likely to expand further, shaping industries and transforming everyday life.
The Road Ahead
As AI continues to evolve, the journey ahead involves addressing challenges while maximizing its potential benefits. Striking a balance between technological innovation and ethical considerations remains imperative. Safeguarding against biases in AI algorithms, ensuring data privacy, and fostering transparency in AI systems are pivotal in earning trust and fostering societal acceptance.
Collaboration among governments, industries, academia, and communities is essential to shape policies, regulations, and frameworks governing AI deployment. Embracing AI education and upskilling initiatives becomes crucial to equip the workforce with the necessary skills to thrive in an AI-driven future.
Conclusion
In the tapestry of technological progress, Artificial Intelligence emerges as a pivotal thread weaving its way through various domains of human endeavor. Its significance in 2024 and beyond underscores the transformative potential it holds. Understanding AI’s capabilities, its ethical implications, and harnessing its power for the collective good represent critical milestones in navigating the intricate landscape of this evolving technology.
As AI continues its ascent, society’s readiness to adapt, innovate responsibly, and harness its potential for positive change will shape the trajectory of our future. The journey with AI is not merely about technological advancement but also about the thoughtful integration of these advancements into our lives, ensuring a more inclusive, ethical, and prosperous future for all.