10 Technologies Shaping the Future of Banking

The FSI sector, in general, and banking in particular, are undergoing a technological churn right now. The reasons are twofold: changing customer expectations and improved technological capabilities. Rising competition from fintech startups that use technology to create unique customer experiences around banking and other financial services has forced large banks to respond by innovating themselves. Furthermore, the threat of cybersecurity breaches means that banks need to be more agile than ever before. Today, we will look at ten innovative technologies in banking that are shaping the future. But before we examine each technology, let’s explore why the banking sector is ripe for disruption.
Need for Innovation in the Banking Sector
For a long time, banks have been reluctant to update their systems—and for good reason. The current systems they use are the product of years of continued innovation to meet immediate customer requirements.
However, this has resulted in siloed systems being used for transactions, savings, investments, and loans. This is not suited for the digital age when competition for banks comes from technology-based fintech startups.
Banks and other traditional financial service providers have had to respond with an array of digitization and innovation initiatives. These initiatives employ cutting-edge technologies to ensure a customer-centric perspective rather than the traditional focus on products, real-time intelligent data integration rather than slow analysis performed after the fact, and an open platform foundation.
In this article, we will briefly look at ten technologies that are disrupting banking and financial services (click on any to go directly to the section):
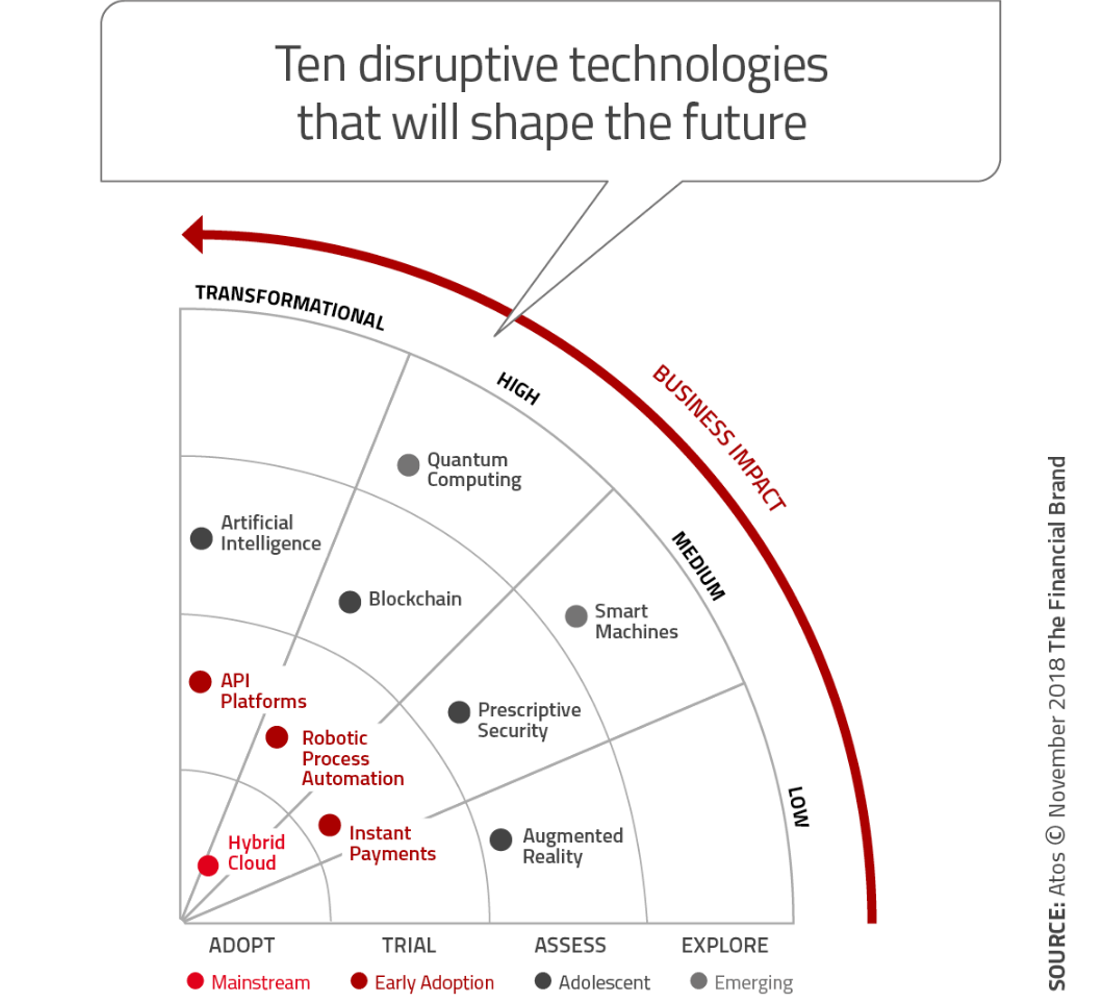
- Augmented Reality
- Blockchain
- Robotic Process Automation
- Quantum Computing
- Artificial Intelligence
- API Platforms
- Prescriptive Security
- Hybrid Cloud
- Instant Payments
- Smart Machines
Atos has created a Global Banking Technology Radar that showcases these technologies beautifully.
10 Banking Technologies That Are Shaping the Future
1. Augmented Reality
Immersive technologies such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality are enhancing customer experiences across various sectors. So why can’t they do the same for banking customers?
The possibilities for implementing augmented reality in the banking sector are limited only by imagination, though these technologies are still in the early stages of development. The goal is to provide customers with complete autonomy in the actions and transactions they perform at home. Technology experts envision hybrid branches, believing that traditional bank branches are becoming a thing of the past.
One of the implementations of augmented reality technology in the banking sector that is already live has been made by the Commonwealth Bank of Australia. They have created a rich data augmented reality application for customers looking to buy or sell a home. It provides them with information such as current listings, recent sales, and price trends to help them make better decisions.
2. Blockchain
Blockchain is a catchall term used to describe distributed ledger technologies. You can think of it as a distributed database with no DBA involved.
It allows multiple parties to access the same data simultaneously while ensuring the integrity and immutability of the records entered into the database. Currently, leading banks around the world are exploring proof-of-concept projects across various aspects of banking and financial services.
The first major implementation we are likely to see is in clearing and settlement. Accenture estimates that investment banks could save $10 billion by deploying blockchain technology to improve the efficiency of clearing and settlement systems.
Another major area where banks will see significant savings using blockchain technology is in KYC (Know Your Customer) operations. Business models being developed could transform KYC from a cost center into a profit center for banks, as they would rely on a shared blockchain for this activity. Syndicated loans, trade finance, and payments are other areas where smart contracts on blockchain could be highly effective.
3. Robotic Process Automation
The volume of unstructured data that banks need to process is increasing exponentially with the rise of the digital economy. This includes not just banking transaction data but also other behavioral data that could potentially allow banks to enhance and innovate customer experience.
This has led bankers to seek technologies that can mimic human action and judgment but with greater speed, scale, and quality. The answer has emerged in the form of a combination of technologies that enable cognitive and robotic process automation in banking.
These technologies include machine learning, natural language processing, chatbots, robotic process automation, and intelligent analytics that allow bots to learn and improve.
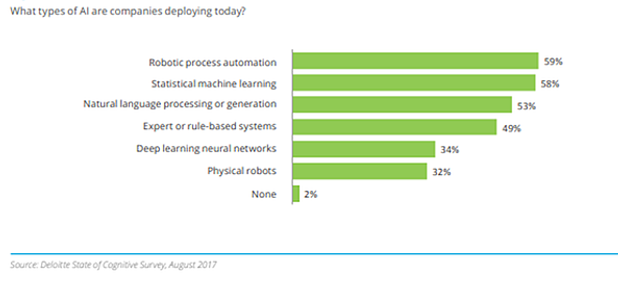
It is no surprise that Deloitte’s 2017 State of Cognitive survey found that 88% of financial service professionals believe such technologies are a strategic priority. That said, the current state of the art in robotic automation is still quite weak in the cognitive and analytical aspects of processes.
In the years to come, we will see current cognitive capabilities being combined with robotic process automation to achieve even better results. This is already being implemented in point-of-sale solutions that automatically suggest marketing promotions that would be most effective for individual customers.
4. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing involves using quantum mechanics to perform complex data operations. Unlike traditional computers that use bits with two values—1 or 0—quantum computing uses “quantum bits” that can have three states: 1, 0, or both. This unlocks exponential computing power compared to traditional computing, provided the right algorithm is used.
Although this represents a significant leap in computing power, commercial implementations are still decades away. Nevertheless, firms like JPMorgan Chase and Barclays are investing in quantum computing research in partnership with IBM.
5. Artificial Intelligence
The explosive growth over the last decade in the amount of structured and unstructured data available to banks, combined with advances in cloud computing and machine learning technologies, has created a perfect environment for Artificial Intelligence (AI) to be utilized across the banking and financial services landscape.
As business needs and AI capabilities have evolved, banks are increasingly viewing AI as a differentiator to outperform emerging competition. AI allows banks to leverage large volumes of data to make better decisions across various functions, including back-office operations, customer experience, marketing, product delivery, risk management, and compliance.
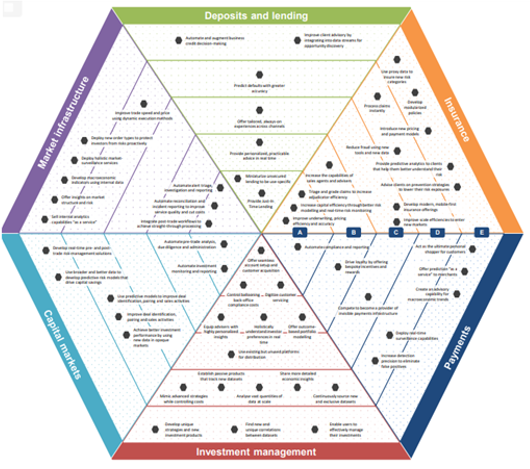
The WEF report “The New Physics of Financial Services” identifies sector-specific opportunities that AI deployment will open up in banking and financial services. These opportunities span deposits, lending, payments, investment management, capital markets, and market infrastructure.
AI is poised to revolutionize banks by shifting the focus from the scale of assets to the scale of data. Banks will aim to deliver tailored experiences to their customers rather than producing mass-market products. Instead of retaining customers through high switching costs, banks will become more customer-focused and retain them by providing significant retention benefits. Most importantly, banks will no longer rely solely on human ingenuity to improve their services. Performance will be a result of the interplay between technology and talent.
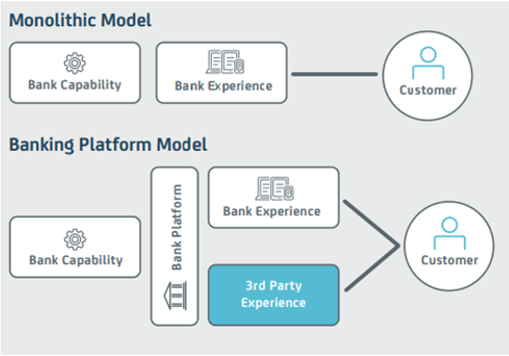
6. API Platforms
The era when banks could control the entire customer experience through a monolithic system that managed everything from record-keeping to every customer interaction is long gone. Both regulatory requirements and evolving customer needs have rendered these enormous systems obsolete.
Today, banks need to build “banking stacks” that serve as platforms to which customers and third-party service providers can connect, delivering a flexible and personalized experience to the end user. To achieve this, they can use API platforms for banking.
An API Banking Platform is designed to function through APIs that sit between the bank’s backend systems and the front-end experiences provided either by the bank itself or third-party partners.
This setup allows banks to adopt entirely new business models and use cases (for example, enabling salary advances) and experiment with new technologies like blockchain at a lower cost. APIs also help banks future-proof their systems by decoupling the front-end from the backend.
7. Prescriptive Security
The nature of cyber risk changes rapidly, making traditional approaches to risk management obsolete. It is now clear that organizations cannot eliminate all possible sources of cyber threats; instead, limiting the attack footprint as early as possible is the best approach. Banks must be agile in their approach to cybersecurity.
Increasingly, banks are deploying advanced analytics, real-time monitoring, and AI to detect threats and prevent them from disrupting their systems. The use of big data analysis techniques to gain early visibility of threats and act to stop them before they materialize is known as prescriptive security.
While implementing this new technique may initially increase vulnerability, it is a necessary step to address the growing number of data breaches reported by various organizations.
8. Hybrid Cloud
One of the biggest challenges the digital age has brought to banking is the need for rapid responsiveness. The constantly evolving market requires banks to be as agile as possible, providing resources across the enterprise in a timely manner to address business problems more quickly.
High-performing banks have discovered that the most cost-effective way to achieve this is through an enterprise-wide hybrid cloud. This approach allows them to leverage the benefits of both public and private clouds while addressing issues such as data security, governance, and compliance, and providing the ability to mobilize large resources in minutes.
A hybrid cloud also enables banks to offer innovative new services to their customers. For example, ICICI Bank has partnered with Zoho to help businesses automate basic reconciliation processes through Zoho Books, a cloud accounting software. This partnership eliminates the need for data entry and facilitates offering multiple payment options to customers.
9. Instant Payments
As the world moves towards a less-cash economy, customer expectations around payments have changed dramatically. Both customers and businesses now expect payments to occur instantaneously, which is where instant payment systems come into play.
Instant payments are essential if online transactions are to replace cash transactions. Therefore, banks worldwide are finding ways to offer their customers options for instant payments, even when the necessary infrastructure is lacking.
For example, banks in Kenya are partnering to provide a P2P payment experience for their customer base. We are likely to see banks integrating their instant payment capabilities with third-party e-commerce and m-commerce solutions to develop new service portfolios.
10. Smart Machines
You may have already seen assistants like Amazon’s Alexa and Google Home in action. Imagine the impact these could have on banking applications.
In fact, Bank of America has already developed Erica, a virtual assistant specifically for banking operations. These smart machines are starting to act as digital concierges for customers interacting with banks.
Banks will need to invest in digital engagement to build long-lasting relationships with customers. Remember, customers will gravitate towards banks that offer the easiest interactions with technologies they have become accustomed to.
Summing It Up
According to a survey of bankers conducted by PwC: “Respondents say skills in their organizations lag across a range of highly important areas, including cybersecurity and privacy, business development of new technologies, and user experience and human-centered design. Worse, skill levels have declined even as the demands of digital keep advancing.”
As banks recognize this skill gap, which hinders their ability to transform and leverage technology, they are beginning to invest significantly in the banking technologies most relevant to their business models.
For example, while blockchain may not be a priority for most industries today, banks and financial institutions see great potential in its implementation. Consequently, the financial services industry views blockchain as a high-priority investment.
Furthermore, as the banking industry evolves, it is imperative that technology becomes a “core competency” with enterprise-wide engagement. The focus on technology cannot be limited to top executives or an isolated IT department.
Finally, the focus of technology implementation should be on customer experience—not just revenue or cost savings. While those are important, they will follow naturally if you can retain customers over the long term.
In the future, bankers will need to view FinTech startups as partners rather than competitors. A bank can be a significant customer for a FinTech company and help them reach new customer bases.
Developing a banking platform will be crucial in achieving better customer satisfaction. Bankers should aim to create new business models where they own customer relationships and leverage FinTech resources from around the globe to generate the most value for the end customer.