What is SaaS (Software as a Service)?

Software as a service is a way of delivering centrally hosted applications over the internet as a service. SaaS applications are sometimes known by other names:
- Web-based software
- On-demand software
- Hosted software
According to TechTarget, “In the software on demand SaaS model, the provider gives customers network-based access to a single copy of an application that the provider created specifically for SaaS distribution.” This application runs on the SaaS provider’s servers, freeing the software’s users from a number of responsibilities.
Step up your business tech with SaaS (Software as a Service)
Traditional business software is installed on individual computers and takes an admin to maintain and update. It can limit businesses when different departments need to collaborate, work from a communal database, or update data on a continuous basis.
This is where cloud computing steps in. The cloud is, in its most basic form, “software, data storage, and processing power” available over the internet. Instead of installing software directly onto your computer, programs are available through a website or app. This type of software is called software as a service, or SaaS. Not every piece of software is available over the cloud, but for most businesses, using software as a service helps keep them ahead of their competition.
12 Business Advantages of Cloud Computing, The Power Behind SaaS (Software as a Service)
On this page, we share the basics of SaaS. This technology is far more advanced than we’ll go into here, but you can read on to learn more about the basics of software as a service, including:
- A more in-depth look at the concept of SaaS
- What SaaS can do for your company
- How SaaS is different from traditional, onsite software
- The benefits of SaaS
- A look at SaaS in action
How SaaS (Software as a Service) can serve your company?
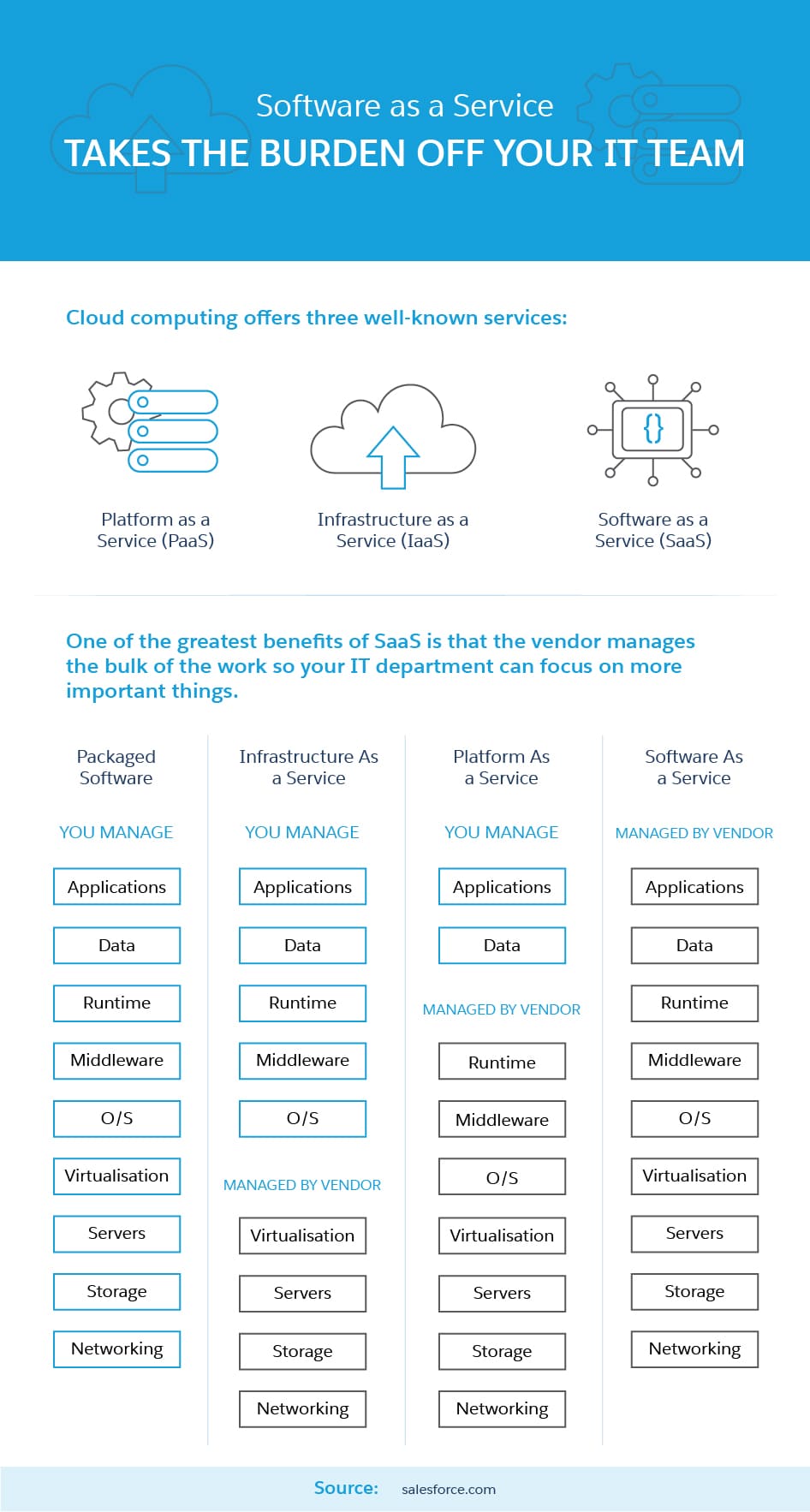
Instead of installing and maintaining software, with software as a service, you simply log in to it with a device that can access the internet. The provider manages everything related to the application, including security, availability, storage, and performance. This frees your information technology (IT) department from complex software and hardware management, which lets them focus on more important duties.
Software as a service is different
Traditional software, also known as on premises or on prem, is generally a large, upfront expense with limited installations. Updates come in the form of new versions of the software that must be paid for and installed again. Computers and a company’s servers must have the capacity to store the application and all its data, and if anything goes awry with the hardware or software, the user has to fix it. Even something as random as a power outage can completely disrupt usage.
SaaS, on the other hand, is often a subscription-based service with pricing options for single or multitenancy — multiple users who can access and use the program simultaneously. Any updates, large or small, can be performed automatically and are part of the service. The SaaS provider often offers training so users can get the most out of their investment, and because the software is housed on the provider’s servers, all the user has to maintain is a connection to the internet.
What are the advantages of SaaS (Software as a Service)?
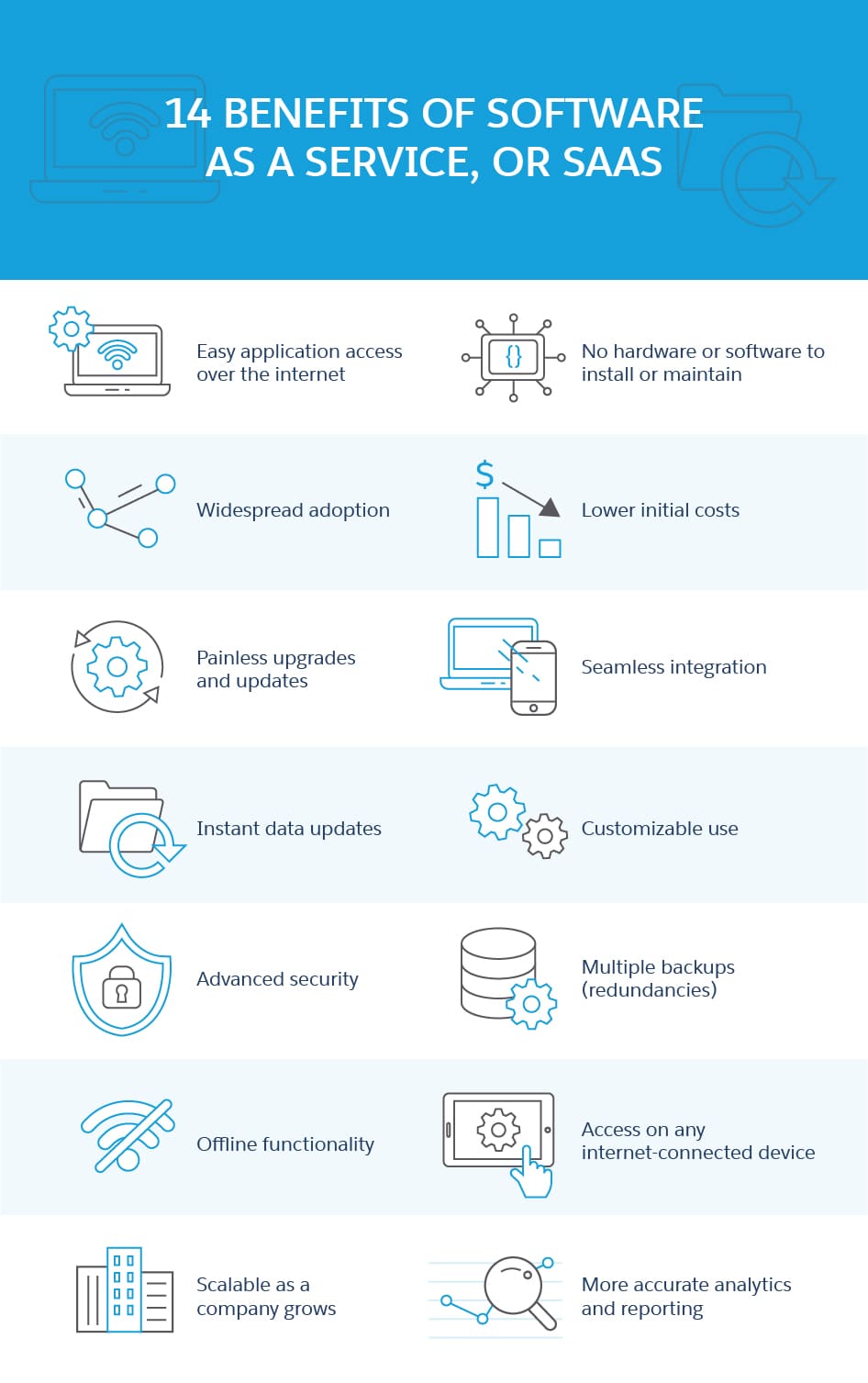
SaaS facilitates remote application hosting and delivery, making this the key advantage of SaaS: painless application access. Customers who use software as a service have no hardware or software to install, maintain, or upgrade. Access to these applications is easy because you just need an internet connection.
- Additional benefits of SaaS include:
- Widespread adoption
- Lower initial costs
- Painless upgrades and updates
- Seamless integration
- Instant data updates
- Customizable use
- Advanced security
- Multiple backups (redundancies)
- Offline functionality
- Access on any internet-connected device
- Scalable as a company grows
- More accurate analytics and reporting
An example of SaaS in action: the suite of Salesforce solutions
Marc Benioff, a co-founder of Salesforce, started the company in 1999 with a “mission to ‘End Software’ through his creation of the ‘cloud.’” What he created was a new kind of software: programs that were immediately available online. With this vision he created SaaS, revolutionized business technology, and likely cleared the path to big data and analytics.
A growing small business can invest in the Salesforce customer relationship management (CRM) platform, which runs Sales Cloud and Quip. The CRM platform is the centralized location for all a company’s data as it grows, with Sales Cloud serving as a specific tool for the sales team that manages every aspect of the sales process. Quip is a collaboration tool built directly into Salesforce that allows multiple users to access and update documents and other files at the same time.
The business owner initially pays for three seats: one for the owner, one for the sales manager, and one for the second salesperson. In six months, when the business has expanded, the owner upgrades to 10 seats and adds another platform to the mix: Marketing Cloud, for the new marketing team. The employees all use laptops and can work remotely as needed. Even when one salesperson is thousands of miles away, they can collaborate on documents and update cases so the marketing team at the home office has accurate data at all times. At an important meeting with an investor, the owner pulls out their smartphone, opens the Salesforce mobile CRM app, and answers investors’ questions with current data.
All decisions regarding business growth are based on dashboards that report accurate data at all times. Because the company is running a fully integrated system, sales, marketing, customer service, and anyone who uses the CRM platform all have access to the same information: a single customer view.
Software as a Service (SaaS) empowers your company to be better
There’s a reason SaaS has become the dominant software model: Its advantages for both providers and customers are numerous. While Salesforce was among the first companies to deploy cloud-based software, today it is by no means the only one, and the cloud has even more to offer companies. However, the most common use is SaaS, and software providers that use this technology are helping empower businesses to be more efficient, agile, and in charge of the customer journey.
Source: https://www.salesforce.com/saas/
Tags
Bestarion Website Admin



