Bestarion USA
Trusted ITO & BPO Service Provider
Security-first, compliance-driven ITO & BPO that streamlines operations and unlocks scalable value
Download Portfolio
















What We Serve
Explore Our Services
Software Development
Software Development

Software Maintenance
Software Maintenance
Software Support
Software Support

Software Testing
Software Testing
DevOps Development
DevOps Development
AI Chatbot Development
AI Chatbot Development
IT Staff Augmentation
IT Staff Augmentation
Data Analytics
Data Analytics
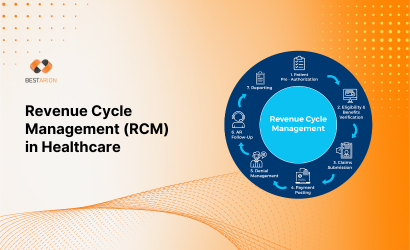
Healthcare
Streamline operations, boost revenue, and enhance patient care with Bestarion’s expert healthcare services.

Supply Chain
Optimize logistics, cut lead time, and boost end-to-end visibility with data-driven engineering.

Manufacturing
Digitize the shop floor, reduce downtime, and raise quality with IoT-enabled solutions for Manufacturing.

E-Commerce
Lift conversion, personalize CX, and automate operations with AI-ready platforms for e-commerce.
Trading
Accelerate deal flow, unify market data, and control risk with low-latency systems for Trading.
Fintech
Ship faster, stay compliant, and scale securely with cloud-native engineering for Fintech.
Banking
Modernize core systems, strengthen security, accelerate digital channels with grade engineering.
Education
Build engaging learning platforms, streamline admin, and scale safely with EdTech expertise for Education.
Global SMEs & Large Enterprises
We have 20+ years of experience providing IT services for pivotal industries, including Healthcare, Finance & Banking, Retail & E-commerce, and Education, that need:
- Full-cycle software development
- IT Staffing
- Data Management & Analytics Solutions
- GenAI & AgentAI
Staff Augmentation
Our developers in your team
Complement specifically skilled professionals to your in-house team. Maximize your coding capacity during periods of growth. Scale up and down at your discretion.
Dedicated Team
Our teams in your organization
Bestarion offers specialized hiring for many industries. We provide a dedicated team that integrates with your teams and works on the project, sharing risks and quality responsibility.
Full Project Outsourcing
Our PM and development teams building for you
You entrust end-to-end software development projects to Bestarion. You can save up to 30% on development costs with our help in selecting and managing people, designing the project, and coordinating all tasks.
Build Operate Transfer
Everything is set up and ready for transfer to you
We build, operate the facility in your best interests, and when the time is suitable, we facilitate a smooth transfer as you assume ownership of it.
Accounting and Bookkeeping
Accounting and Bookkeeping
Tax Preparation
Tax Preparation
Payroll Processing
Payroll Processing
Data Entry
Data Entry
Healthcare
Streamline revenue cycle, cut admin load, and elevate patient CX with HIPAA-ready back-office for Healthcare.

Retail & Wholesale
Optimize order-to-cash, sync inventory and catalogs, and speed fulfillment with omnichannel back-office for Retail & Wholesale.

Food & Beverage
Standardize procurement, ensure QA documentation, and tighten traceability/ compliance with cost-efficient back-office.

Supermarket
Automate price updates, reconcile inventory, and manage promotions/loyalty ops with store-ready back-office for Supermarkets.
Insurance
Accelerate claims intake, support underwriting, and streamline policy admin with compliant, audit-ready back-office for Insurance

Software
Scale billing & collections, centralize data ops, and elevate tier-1 support with back-office for Software.
Legal Services
Speed document review, abstract contracts, and optimize billing/ docketing with secure, confidential back-office.
Logistics
Digitize paperwork, track shipments proactively, and improve cash cycle with 24/7 back-office for Logistics providers.
U.S. CPA, Accounting & Tax Firms
We have 7+ years of experience handling all their accounting tasks with tailored outsourced accounting services, including:
- White-label Bookkeeping, Payroll & Tax Preparation
- Full-time Equivalent
- Accounting Staffing
FTE
We provide a dedicated offshore accountant who functions as a full-time equivalent for your business to handle a defined set of financial accounting tasks based on your needs at a fraction cost of hiring an in-house U.S.-based staff.
-
Steady workloads
-
Knowledge retention
-
24/7 Ops
Utilization
Accuracy
Hourly Rate
Clients are billed based on the actual time accountants spend on tasks. Costs are determined by the number of hours worked, making this model suitable for projects with flexible or evolving requirements.
-
Scope fluidity
-
Pilots
-
R&D
Burn rate/ NTE
Accuracy
Value-Based
We are charged based on the scope and complexity of specific tasks, such as the number of transactions processed, payrolls managed, or financial reports generated, rather than the time spent completing them.
-
Standardized processes
-
Seasonal volumes
FPY
% SLA
Cost per unit
Why Choose Us
In The Best We Trust
Years Experience
Employees
Successful Projects
Satisfaction Rate





Measurable Cost Efficiency
Reduce TCO with outcome aligned delivery and transparent unit economics across applications and back-office workflows.
TCO %
Unit Cost
How We Do
We Deliver Better Solution for Less

Healthcare Supply Chain

The team is doing a great job setting delivery dates and meeting them. Many thanks to the team for being a part of Meperia! Let’s keep that up!
Overall Review Rating
Staff time to fix errors post-purchase
Occurrence rate of difference prices paid for same product
Item master content churn outdates
Over payments are made on costly Physician Preference Items
Saving annual supply chain spending
Usage by US healthcare facilities








Number of Statement
Number of Clients Released
Accuracy Rate
Team Members
Years of cooperation








Latest Insights
Find Out Our Insights
Contact Us
Start Your Project Today and Watch Your Business Grow
Drop us a line.
We'll hear from you soon.
Our Advantages
- 21+ years of providing software solutions development services for global businesses.
- 6+ years of providing accounting outsourcing services for CPA firms in the US.
- 215+ released projects
- 150+ in-house specialists
- Valuable suggestions from experts in the field for your project.
USA
1005 Congress Avenue, Suite 925-E35, Austin, TX 78701