Integration Testing: Definition, Types & Examples


What is Integration Testing?
Integration testing is a type of testing in which software modules are logically integrated and tested as a group. A typical software project consists of several software modules written by various programmers. The goal of this level of testing is to identify flaws in the interaction of these software modules when they are combined.
Integration testing examines data communication between these modules. As a result, it is also known as “I&T” (Integration and Testing), ‘String Testing’ and sometime ‘Thread Testing.’
Why should you perform Integration Testing?
Although each software module is unit tested, defects do exist for a variety of reasons, including:
- In general, a Module is created by an individual software developer whose understanding and programming logic may differ from that of other programmers. Integration testing is required to ensure that the software modules work together.
- There is a high possibility of client requirements changing during module development. Because these new requirements may not be unit tested, system integration testing is required.
- Interfaces between software modules and databases may be incorrect.
- External hardware interfaces, if present, could be incorrect.
- Inadequate exception handling may cause problems.
Integration Test Case Example
The Integration Test Case differs from other test cases because it focuses on the modules’ interfaces and data/information flow. Priority should be given to integrating links rather than unit functions that have already been tested.
Integration Test Case Examples for the Following Scenario: The application has three modules: ‘Login Page,’ ‘Mailbox,’ and ‘Delete Emails,’ all of which are logically integrated.
Because it has already been done in Unit Testing, do not focus much on Login Page testing here. However, note how it is linked to the Mail Box Page.
Mail Box: Examine its integration with the Delete Mails Module.
| Test Case ID | Test Case Objective | Test Case Description | Expected Result |
| 1 | Check the interface link between the Login and Mailbox module | Enter login credentials and click on the Login button | To be directed to the Mail Box |
| 2 | Check the interface link between the Mailbox and Delete Mails Module | From Mailbox select the email and click a delete button | Selected email should appear in the Deleted/Trash folder |
Read more: Unit Testing in Software Testing: Types, Tools & Best Practices
Integration Testing Types
Software engineering defines several strategies for carrying out integration testing, such as:
- Big Bang Approach:
- Incremental Approach: which is further divided into the following
- Top Down Approach
- Bottom-Up Approach
- Sandwich Approach – Combination of Top Down and Bottom Up
The following are the various strategies, their implementation, and their limitations and advantages.
Big Bang Testing
Big Bang Testing is an approach to integration testing in which all components or modules are integrated simultaneously and then tested as a unit. During testing, this combined set of components is treated as an entity. The integration process will fail if all of the components in the unit are not completed.
Advantages: Ideal for small systems.
Disadvantages:
- Localization of faults is difficult.
- Given the sheer number of interfaces that must be tested in this Approach, some interfaces may be overlooked.
- Because integration testing can only begin after “all” modules have been designed, the testing team will have less time for execution during the testing phase.
- Because all modules are tested at the same time, high-risk critical modules are not isolated and tested first. Peripheral modules dealing with user interfaces are also not isolated and prioritized for testing.
Incremental Testing
The Incremental Testing approach involves integrating two or more modules logically related to each other and testing the application for proper operation. The other related modules are then incrementally integrated, and the process is repeated until all logically related modules have been successfully integrated and tested.
The Incremental Approach, on the other hand, is carried out by two different methods:
- Bottom Up
- Top Down
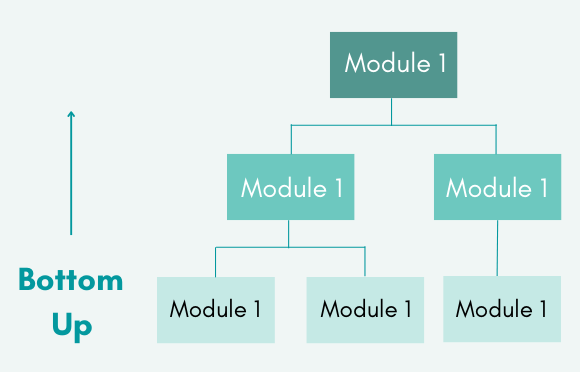
Bottom-up Integration Testing
Bottom-up Lower level modules are tested first in an integration testing strategy. These tested modules are then used to speed up the testing of higher-level modules. The process is repeated until all top-level modules have been tested. The next level of modules is formed after the lower level modules have been tested and integrated.
Diagrammatic Representation:
Advantages:
- Fault localization is easier.
- Unlike the Big-bang approach, no time is wasted waiting for all modules to be developed.
Disadvantages:
- Critical modules (at the highest level of software architecture) that control the application flow are tested last and may have flaws.
- An early prototype is not possible.
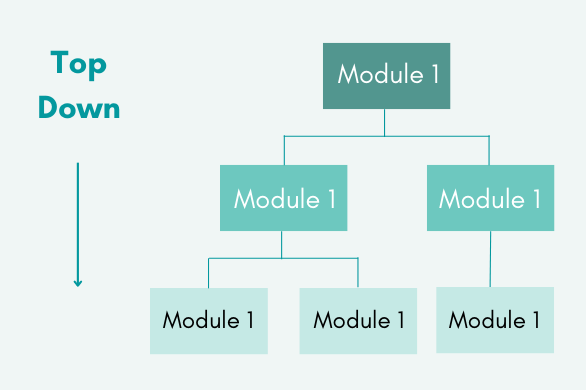
Top-down Integration Testing
Top Down Integration Testing is a method of performing integration testing from top to bottom following the control flow of a software system. Higher-level modules are tested first, followed by lower-level modules to test the software functionality. If some modules are not yet ready, stubs are used for testing.
Diagrammatic Representation:
Advantages:
- Fault Localization is easier.
- Possibility to obtain an early prototype.
- Critical Modules are tested on priority; major design flaws could be found and fixed first.
Disadvantages:
- Needs many Stubs.
- Modules at a lower level are tested inadequately.
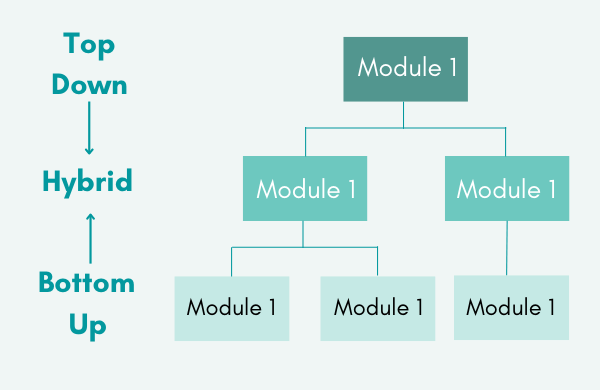
Sandwich Testing
Sandwich testing is a strategy in which top-level modules are tested alongside lower-level modules. In contrast, lower modules are integrated and tested as a system. Because it combines top-down and bottom-up approaches, it is known as Hybrid Integration Testing. It employs the use of both stubs and drivers.
Stubs and Drivers
Stubs and Drivers are dummy programs used in integration testing to help with software testing. These programs serve as stand-ins for missing models in testing. They do not implement the entire software module’s programming logic but instead simulate data communication with the calling module while testing.
- Stub: Is called by the Module under Test.
- Driver: Calls the Module to be tested.
Read more: What is Regression Testing? Definition, Tools and How to Begin
How to Perform Integration Testing
Regardless of the Software testing strategies (discussed above), the Integration test procedure is as follows:
- Make a plan for the integration tests.
- Creating Test Scenarios, Cases, and Scripts
- Running the test Cases is followed by defect reporting.
- Defect tracking and re-testing
- Steps 3 and 4 are repeated until integration is completed.
A Synopsis of Integration Test Plans
It has the following characteristics:
- Testing Methods and Approaches (as discussed above).
- Integration Testing Scopes and Out-of-Scope Items
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Integration testing prerequisites
- Environment for testing
- Risk and Mitigation Strategies
Integration Testing Entry and Exit Criteria
Entry Criteria:
- Components/Modules That Have Been Unit-Tested
- All High Priority bugs have been fixed and closed.
- All modules must be coded and successfully integrated.
- Plan, test cases, and scenarios for integration tests must be signed off and documented.
- Integration testing necessitates the establishment of a test environment.
Exit Criteria:
- Successful Testing of Integrated Application.
- Executed Test Cases are documented.
- All High prioritized bugs were fixed and closed.
- Technical documents to be submitted, followed by release Notes.
Best Practices/ Guidelines for Integration Testing
- Determine the Integration Test Strategy that could be used first, and then prepare the test cases and data accordingly.
- Examine the application’s architecture design and identify the critical modules. Priority should be given to testing these.
- Obtain the interface designs from the Architectural team and write test cases to test all of the interfaces thoroughly. The database/external hardware/software application interface must be thoroughly tested.
- The test data comes second to the test cases in importance.
- Before executing, always have the mock data ready. When running the test cases, do not select test data.
Enhance Your Product Quality With Our Software Testing Services
At Bestarion, we understand that the success of your software project depends not only on its functionality but also on its reliability, performance, and overall quality. That’s why we offer a comprehensive suite of software testing services designed to address every challenge and ensure your product meets the highest standards. Our approach is tailored to your specific needs, providing custom quality assurance management plans that guarantee speed, precision, and excellence throughout the development lifecycle.
Our Comprehensive Testing Services
Bestarion provides a broad range of software testing services to cover all aspects of your project. Whether you’re developing a web application, mobile app, or desktop software, our testing services are designed to meet your needs.
1. Functional Testing
Functional testing focuses on verifying that your software performs its intended functions correctly. We test individual components and entire systems to ensure they meet the specified requirements. Our functional testing includes:
- Unit Testing: Examines individual components or modules for correctness.
- Integration Testing: Assesses the interactions between integrated modules or systems.
- System Testing: Validates the complete and integrated software system to ensure it meets all requirements.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Ensures the software meets the end-user requirements and expectations.
2. Performance Testing
Performance testing evaluates how your software performs under various conditions. It helps identify bottlenecks and ensures your application can handle the expected load. Our performance testing services include:
- Load Testing: Determines how the system performs under expected load conditions.
- Stress Testing: Assesses the system’s behavior under extreme conditions or overloads.
- Scalability Testing: Evaluates how well the software can scale with increasing data volume or user load.
- Endurance Testing: Checks the system’s stability and performance over an extended period.
3. Security Testing
Security testing is essential to protect your software from vulnerabilities and potential threats. Our security testing services include:
- Penetration Testing: Simulates attacks to identify vulnerabilities and assess the system’s defenses.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Identifies and evaluates security weaknesses in the application.
- Security Code Review: Examines the source code for security flaws and vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Testing: Ensures the software meets industry standards and regulatory requirements.
4. Compatibility Testing
Compatibility testing ensures your software functions correctly across different environments, including various operating systems, browsers, and devices. We test for:
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: Verifies that web applications work across different browsers.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Ensures applications perform consistently on various operating systems.
- Device Compatibility: Tests the application on different devices to ensure proper functionality.
5. Usability Testing
Usability testing focuses on the user experience, ensuring the software is intuitive, user-friendly, and meets the needs of its target audience. Our usability testing services include:
- User Interface (UI) Testing: Evaluates the software’s interface for ease of use and aesthetic appeal.
- User Experience (UX) Testing: Assesses the overall experience of using the software, including navigation, interaction, and satisfaction.
6. Regression Testing
Regression testing is performed to ensure that recent changes or enhancements do not adversely affect the existing functionality of the software. We re-test the software to confirm that it continues to perform as expected after modifications.
7. Automation Testing
Automation testing utilizes tools and scripts to perform repetitive testing tasks efficiently. It accelerates the testing process and improves accuracy. Our automation services include:
- Test Script Development: Creating and maintaining automated test scripts.
- Test Automation Frameworks: Implementing frameworks to support automated testing processes.
- Continuous Integration Testing: Integrating automated tests into the development pipeline for ongoing quality assurance.
Custom Quality Assurance Management Plans
At Bestarion, we recognize that every project is unique. That’s why we create custom quality assurance management plans tailored to your specific needs. Our plans include:
- Defining Testing Objectives: Establishing clear goals and criteria for testing based on your project requirements.
- Developing Test Strategies: Crafting comprehensive strategies that outline the testing approach, methodologies, and tools.
- Creating Test Cases: Designing detailed test cases to ensure thorough coverage of all functionalities.
- Executing Tests: Conducting tests according to the plan and documenting the results.
- Reporting and Feedback: Providing detailed reports on testing outcomes, defects, and recommendations for improvements.
Supporting Your Evolving Platforms
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, platforms are constantly evolving. Bestarion is committed to supporting your software as it grows and adapts. Our ongoing support includes:
- Regular Testing Updates: Continuously updating and executing tests as your software evolves.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Monitoring the performance and security of your software and performing maintenance as needed.
- Adapting to Changes: Adjusting our testing approach to accommodate new features, updates, and changes in technology.
Why Choose Bestarion?
- Expertise: Our team of experienced testers brings a wealth of knowledge and expertise to every project.
- Customized Solutions: We tailor our testing services to meet your specific needs and objectives.
- Advanced Tools and Techniques: We utilize the latest testing tools and techniques to deliver accurate and efficient results.
- Commitment to Quality: Our focus is on ensuring the highest quality of your software, from development through deployment.
Ready to enhance your product quality? Contact Bestarion today to discover how our tailored software testing solutions can drive your project’s success!