Bridging IaaS and PaaS

The rapid advancement of cloud computing has transformed how businesses operate, providing unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. Among the various cloud service models, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) stand out as crucial components. While IaaS offers virtualized computing resources over the internet, PaaS provides a platform allowing developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. Bridging IaaS and PaaS can lead to a more integrated and seamless cloud environment, enhancing the overall capabilities of businesses. This article explores the synergy between IaaS and PaaS, examining their individual strengths, the benefits of bridging them, and the potential challenges.
Read more: Cloud Data Warehouses: The Future of Data Management
Understanding IaaS and PaaS
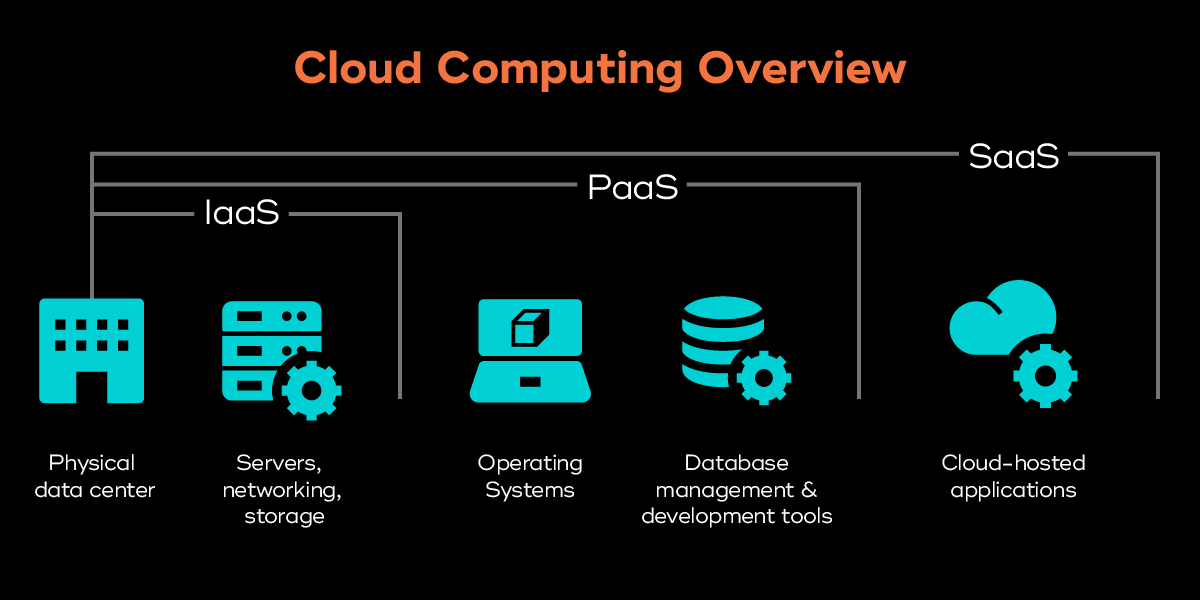
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is the foundational layer of cloud computing, providing virtualized computing resources over the internet. It includes virtual machines, storage, networks, and other fundamental computing resources. Key characteristics of IaaS include:
- Scalability: IaaS allows businesses to scale their infrastructure up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By leveraging IaaS, companies can avoid the capital expenditure associated with maintaining physical hardware, opting for a pay-as-you-go model.
- Flexibility: IaaS provides a high degree of control over the infrastructure, allowing businesses to customize their environment to meet specific needs.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS sits atop IaaS, offering a platform that enables developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without dealing with the complexities of infrastructure management. Key characteristics of PaaS include:
- Development Efficiency: PaaS provides pre-configured environments, frameworks, and tools that streamline the development process.
- Simplified Deployment: PaaS platforms often include automated deployment and scaling features, reducing the time and effort required to bring applications to market.
- Integrated Services: PaaS offers a range of integrated services, such as databases, messaging, and monitoring, enhancing the functionality of applications.
The Synergy Between IaaS and PaaS
Combining IaaS and PaaS can lead to a more cohesive cloud strategy, leveraging the strengths of both models. Here are some of the key benefits of bridging IaaS and PaaS:
Enhanced Flexibility and Control
While PaaS simplifies application development and deployment, IaaS offers granular control over the underlying infrastructure. By integrating the two, businesses can achieve a balance between ease of use and customization. Developers can leverage the automated and pre-configured environments of PaaS while retaining the ability to fine-tune the infrastructure as needed through IaaS.
Cost Optimization
Bridging IaaS and PaaS allows businesses to optimize costs by leveraging the pay-as-you-go model of IaaS for infrastructure resources and the streamlined development capabilities of PaaS. This integration ensures that resources are used efficiently, reducing waste and lowering overall expenses.
Accelerated Development and Deployment
PaaS platforms provide a range of development tools, frameworks, and services that accelerate the application development process. When combined with the scalable infrastructure of IaaS, businesses can quickly deploy and scale applications to meet demand. This synergy results in faster time-to-market and improved agility.
Improved Resource Management
Integrating IaaS and PaaS enables better resource management by providing a unified view of infrastructure and application performance. This holistic approach allows businesses to monitor and optimize resource usage, ensuring that applications run efficiently and reliably.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Both IaaS and PaaS providers offer robust security features, including encryption, identity management, and compliance certifications. By bridging these models, businesses can create a comprehensive security strategy that addresses both infrastructure and application-level concerns, ensuring data protection and regulatory compliance.
Use Cases of Bridging IaaS and PaaS
Enterprise Application Development
For large enterprises, developing and deploying applications often require a complex and scalable infrastructure. By integrating IaaS and PaaS, enterprises can leverage the scalability of IaaS to handle large volumes of data and users, while PaaS streamlines the development and deployment process. This approach enhances collaboration, reduces development cycles, and ensures that applications can scale seamlessly as demand grows.
Startups and Small Businesses
Startups and small businesses can benefit significantly from the cost-effective and scalable nature of IaaS combined with the development efficiency of PaaS. This integration allows them to quickly build and deploy applications without significant upfront investment in infrastructure. Additionally, the ability to scale resources on-demand ensures that they can handle growth without overcommitting resources.
Hybrid Cloud Environments
Many organizations operate in hybrid cloud environments, utilizing both on-premises infrastructure and cloud services. Bridging IaaS and PaaS in such environments enables seamless integration between on-premises and cloud resources. This approach allows businesses to leverage existing investments in infrastructure while taking advantage of the flexibility and scalability of cloud services.
DevOps and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
DevOps practices rely on automation and collaboration to streamline the software development lifecycle. Integrating IaaS and PaaS supports DevOps by providing automated infrastructure provisioning and application deployment. This approach enables continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), ensuring that new features and updates can be rolled out rapidly and reliably.
Challenges of Bridging IaaS and PaaS
While the benefits of bridging IaaS and PaaS are significant, there are also challenges that businesses must address:
Complexity of Integration
Integrating IaaS and PaaS requires careful planning and execution to ensure seamless interoperability. Businesses must navigate the complexities of connecting different platforms, managing dependencies, and ensuring compatibility. This process can be time-consuming and requires expertise in both infrastructure and application development.
Vendor Lock-In
Relying on a single provider for both IaaS and PaaS can lead to vendor lock-in, limiting flexibility and increasing dependency on a specific vendor’s ecosystem. To mitigate this risk, businesses should consider adopting multi-cloud strategies or using open-source solutions that provide greater portability and interoperability.
Security and Compliance
While both IaaS and PaaS providers offer robust security features, integrating the two models can introduce new security challenges. Businesses must ensure that their security policies and practices are consistent across both infrastructure and application layers. Additionally, they must address compliance requirements for data protection and privacy, especially when dealing with sensitive information.
Performance Optimization
Achieving optimal performance when bridging IaaS and PaaS requires careful tuning and monitoring of both infrastructure and applications. Businesses must invest in performance management tools and practices to ensure that applications run efficiently and meet user expectations.
Best Practices for Bridging IaaS and PaaS
To successfully bridge IaaS and PaaS, businesses should adopt the following best practices:
Adopt a Holistic Cloud Strategy
Develop a comprehensive cloud strategy that outlines the goals, requirements, and expected outcomes of integrating IaaS and PaaS. This strategy should consider factors such as scalability, cost optimization, security, and compliance.
Leverage Automation and Orchestration
Utilize automation and orchestration tools to streamline the provisioning and management of infrastructure and applications. These tools can help automate repetitive tasks, reduce errors, and ensure consistency across environments.
Implement Robust Security Measures
Develop a unified security strategy that addresses both infrastructure and application-level concerns. Implement encryption, identity management, and access controls to protect data and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Monitor and Optimize Performance
Invest in monitoring and performance management tools to gain visibility into the performance of infrastructure and applications. Use these insights to identify and address bottlenecks, optimize resource usage, and ensure a seamless user experience.
Foster Collaboration and Communication
Encourage collaboration and communication between development and operations teams to ensure a smooth integration of IaaS and PaaS. Adopting DevOps practices can help streamline workflows, improve collaboration, and accelerate the development and deployment process.
Conclusion
Bridging IaaS and PaaS offers a powerful combination of flexibility, scalability, and efficiency, enabling businesses to harness the full potential of cloud computing. By integrating these models, organizations can optimize costs, accelerate development and deployment, and improve resource management. However, businesses must also address the challenges of integration, security, and performance optimization to fully realize the benefits of this approach. By adopting a holistic cloud strategy, leveraging automation, implementing robust security measures, and fostering collaboration, businesses can successfully bridge IaaS and PaaS and drive innovation in today’s competitive landscape.
