Enjoy the Benefits of
Software Testing Services
We help you solve quality issues by reducing risks, maximizing efficiency, and strengthening your organization.
With over 20 years of absolute excellence as a software testing service provider, we’re here to make sure your solution is tested thoroughly, on time, and within budget.
Why is Software Testing Important?
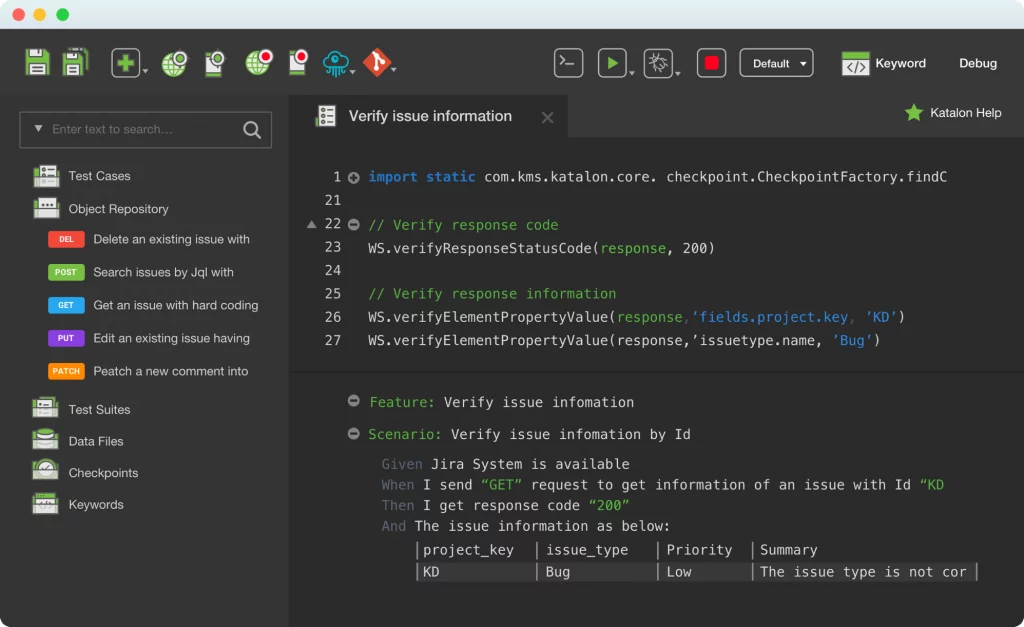
Software testing services aim to ensure that software fully meets requirements and user expectations. Bestarion provides full-range software testing services to help our customers deliver high-quality software meeting tight deadlines of frequent releases.
Early Defect Detection
By integrating QA processes early in the development lifecycle, we identify and resolve defects before they become costly issues.
Improves Product Quality
Software testing ensures that bugs are detected and fixed before your customers get their hands on it.
Enhanced Security
Software security testing promises improved IT risk for the enterprise by removing security vulnerabilities before exploitation.
Faster Speed-to-Market
Continuous testing helps speed up time to market with the best product quality.
Our Services
Software Testing Types We Perform
Bestarion provides comprehensive software testing services for every challenge. We offer various types of testing and create custom quality assurance management plans to ensure your team delivers the highest-quality version of your product with speed and precision. We can support your platforms as they continue to evolve.
Manual Testing
We have experience testing with various software development models and prioritize shift-left testing. The major technique is specification-based (black-box). API testing is considered essential to cover most API response codes.
- Integration Testing
- System Testing
- End-to-End Testing
- Acceptance Testing
Automated Testing
Using trusted automation frameworks, we can help you accelerate releases, increase test coverage and find more bugs before they enter production. Our automation team can provide various test automation solutions for different project contexts and clients.
- Test Automation Frameworks
- Regression Testing
- Smoke Testing
Performance Testing
Performance testing will be conducted to ensure that the payroll system’s response times meet user expectations and do not exceed the specified performance criteria. During these tests, response times will be measured under heavy stress and/or volume.
Mobile Testing
Mobile testing ensures that your application performs optimally across various mobile devices and operating systems, guaranteeing a seamless user experience.
- Cross-Platform Testing
- Responsive Testing
Smoke Testing
Initial check to verify basic functionality.
Sanity Testing
Quick check to ensure specific functions or bug fixes work.
Confirmation Testing
Verifying that previously identified defects have been fixed.
Regression Testing
Ensuring new code changes do not affect existing functionalities.
Usability Testing
Evaluating the ease of use and user-friendliness of the software.
Exploratory Testing
Informal, experience-based testing without predefined test cases.
Compatibility Testing
Ensuring software works across different devices, OS, browsers, etc.
Functional Testing
Verifying each function of the software operates as per the requirements.
UI Testing
Checking graphical user interface elements and interactions.
Localization Testing
Ensuring software functions correctly in different regions and languages.
Accessibility Testing
Ensuring software is accessible to users with disabilities.
Web Application Testing
Evaluating the functionality, usability, security, compatibility, and performance of websites and web applications to ensure they work seamlessly across different browsers, devices, and operating systems.
Mobile Application Testing
Verifying the performance, usability, and functionality of mobile apps across various devices and operating systems (iOS, Android, etc.) to ensure smooth operation on different screen sizes and network conditions.
Desktop Application Testing
Assessing software applications that run on desktop computers and laptops to ensure they perform correctly on various operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux, etc.), hardware configurations, and screen resolutions.
-
Healthcare Supply Chain
-
Banking
-
Logistic
-
Retail / E-commerce
Our Services
Software Testing Service Options
Our testing experts can assist in achieving exceptional software quality within optimal testing time and budget.
Our Services
Agile Software Testing Process
We employ the agile testing approach, an approach that emphasizes smarter testing, delivering high-quality products efficiently. Agile testing speeds up the detection of defects and reduces the cost of bugs by fixing them early. This approach also yields a customer-centric approach by delivering a high-quality product as early as possible. We are also proficient in setting up continuous testing practices and integrating testing activities into CI/CD pipelines within the DevOps approach.
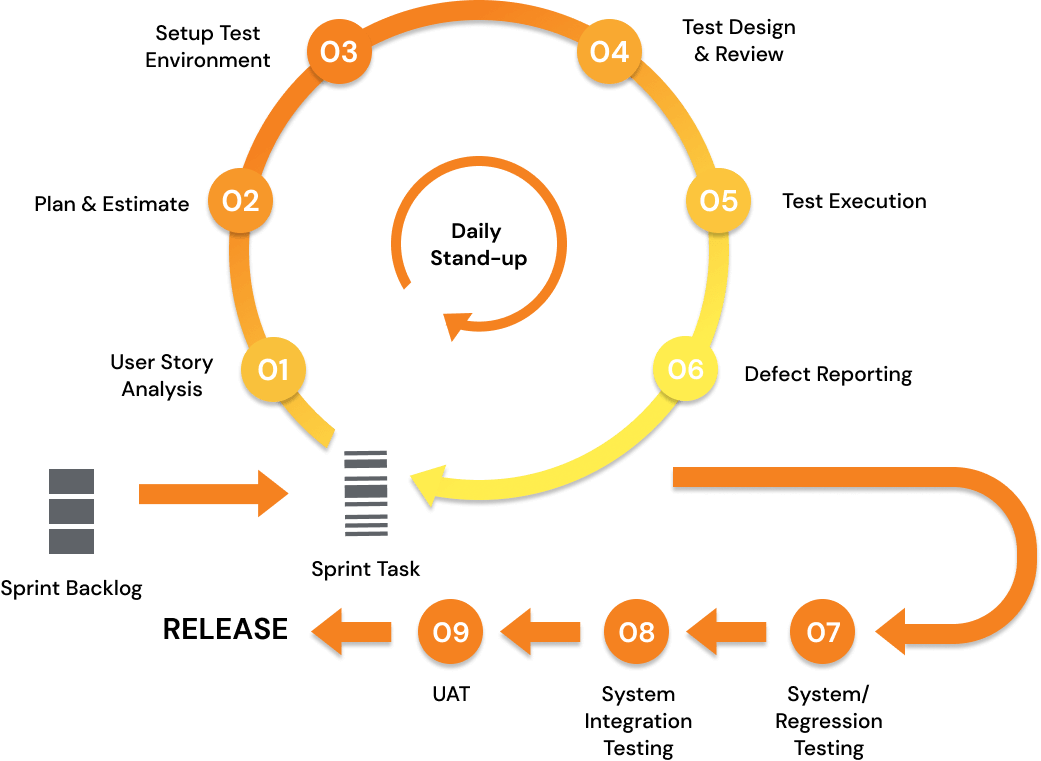


Stand-up







Technologies We Use
Cutting-edge Technology Stack Used by Our Experts

Robot Framework

Jenkins

Test Link

Appium

Postman

Azure Devops
Redmine

Apache Jmeter

PostgreSQL

MySQL
Outsourcing Model
Cooperation Models
Depending on the project complexity and business specifics, we can provide software testing services performed by:
Testing Team Augmentation
We can supplement your testing team with individual testing professionals who will report to your in-house QA manager. This way, you can fill the gap in your in-house QA team’s competencies in a specific technology, industry, testing type, or regulation.
Dedicated Testing Team
Bestarion provides a dedicated testing team comprising a test lead + test engineers that integrates with your teams and works on the project, sharing risks and quality responsibility. The testing teams’ number and composition are flexible and can be scaled up and down depending on your project needs.
Why choose Bestarion for Software Testing Services?
We offer full-cycle software testing services by combining automated testing with manual testing in the real world to optimize testing time and ensure test coverage throughout the entire software development process.
We assist our clients in making the transition to continuous delivery seamlessly by implementing DevOps practices, advanced functional and non-functional testing, and detailed business assurance workflows.
In addition to our strict in-house quality management standards, we're an ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 certified company; we guarantee the high quality of our testing services and the security of customers' data.
Bestarion’s test engineers align the testing activities with your development process to ensure testing time-effectiveness, smooth integration into a CI/CD pipeline, and efficient implementation of risk-based testing.
This has been a big year for MSS, and we have made great progress on a number of areas. Thank you so much and let’s keep it up!

We've got answers
Frequently asked questions
If you're new or looking for answers to your questions, this guide will help you learn more about our services and their features.
Software testing is a systematic evaluation of a product’s quality. Its purpose is to verify that digital products work as intended. For this, QA engineers interact with a program, application, etc., aiming to identify errors, gaps, or discrepancies between its expected and actual behaviors.
During testing, specialists assess different aspects of the software: functionality, performance, security, usability, and compatibility. Testing services for software highlight defects early in the development cycle and fix them before the software is released and becomes available to end-users.
By testing software, QA engineers ensure that a product meets user requirements, performs optimally, and is free of critical errors. If not, finding and fixing the problems enhances the software’s quality and reliability.
In particular, software testing as a service:
- Helps identify, fix, and prevent defects from escalating into more significant problems during later stages or after deployment.
- Ensures that the software meets business and system requirements and other compliance and quality standards.
- Contributes to a positive user experience and higher loyalty by addressing issues that could impact functionality, performance, or usability.
- Plays a vital role in risk mitigation strategy, reducing the likelihood of project delays or failures.
- Allows for minimizing software development and maintenance costs by addressing defects early on.
- Analyses the software’s performance under different conditions, including heavy user loads or varying network speeds, to optimize performance for different scenarios.
- Provides valuable feedback regarding product enhancements, updates, and future iterations.
Testing strongly contributes to the overall success of software projects. Hence, outsourcing software testing services will help you launch high-quality, reliable, and user-friendly products and services.
Software testing and QA (Quality Assurance) services are related to the software development process, but they are different in their goals and focus.
Software testing refers to the process of checking the software application or system to ensure that it works as intended and that it meets the specified requirements. It involves executing the software with different test scenarios and data to identify any defects, errors, or issues that may affect its performance or functionality. Testing can be manual or automated and can include different types of testing such as functional testing, performance testing, security testing, and usability testing.
QA services, on the other hand, encompass a broader range of activities that are designed to ensure that the software development process produces high-quality software that meets the user’s needs and expectations. QA services are concerned with the entire software development life cycle, from requirements gathering and design to coding, testing, and deployment. QA services include activities such as creating quality standards and guidelines, conducting reviews and inspections, performing testing, managing defects and issues, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
In essence, software testing is a specific activity within the broader scope of QA services. Testing focuses on verifying that the software works as intended, while QA services focus on ensuring that the software development process produces high-quality software that meets the user’s needs and expectations.
We always make sure to find at least several common hours. You can be sure you can communicate with QA engineers directly during your working day. If you want to involve QA engineers in the team meetings, it won’t be a problem at all.
Meanwhile, the time difference has its perks for outsourcing software testing services. Namely, when your team has off-work hours, we’re testing. Your teams can see the results, receive reports and tickets, and get something to work with first thing in the morning.
Bestarion is a leading provider of end-to-end software testing services, leveraging global expertise and advanced automation tools to ensure quality, reduced time to market, and optimized costs. Together, we can accelerate digital transformation with reliable and scalable software testing services.
There are many different types of software testing, which can be broadly categorized into the following types:
- Functional Testing: This type of testing checks if the software application or system works as intended and meets the functional requirements.
- Performance Testing: This type of testing checks the software’s performance in terms of speed, scalability, and stability.
- Security Testing: This type of testing checks the software’s security features and identifies any vulnerabilities or threats that could be exploited.
- Usability Testing: This type of testing checks the software’s user interface and user experience to ensure that it is user-friendly and easy to use.
- Compatibility Testing: This type of testing checks the software’s compatibility with different operating systems, hardware, and software configurations.
- Regression Testing: This type of testing checks if changes or updates made to the software do not affect the existing functionality or create new defects.
- Acceptance Testing: This type of testing checks if the software meets the user’s expectations and requirements.
- Integration Testing: This type of testing checks the interaction between different modules or components of the software system.
- Exploratory Testing: This type of testing involves exploring the software application or system to discover defects or issues that were not identified in other testing types. Automated Testing: This type of testing uses automation tools to execute tests and verify the software’s functionality, performance, and security.
Latest News
Get inspired, learn and transform
Stay informed and inspired: discover the freshest blog articles, latest updates, and breaking news.
Optimize Your Projects Using the Software Testing Life Cycle
The software testing life cycle (STLC) is a crucial aspect
Revolutionizing Automated Testing with Generative AI
Generative AI has dramatically reshaped the technological landscape in recent
Revolutionizing Your Process with Outsourcing Software Testing
Software testing services aim to ensure that software fully meets
Start Your Project Today and Watch Business Grow
Get in Touch
Our Advantages
21+ years of providing software solutions development services for global businesses.
5+ years of providing accounting outsourcing services for CPA firms in the US.
215+ released projects
180+ in-house specialists
Needs analysis instead of sales talk
Valuable suggestions from experts in the field for your project.
Vietnam
QTSC Building 1, Street 14, Quang Trung Software City, Tan Chanh Hiep Ward, District 12, HCM City, Vietnam





