Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) in Healthcare: An In-Depth Guide
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is the heartbeat of any healthcare organization’s financial success. While the focus of healthcare will always be on delivering quality care, it’s the behind-the-scenes process of RCM that ensures providers get paid, patients understand their financial obligations, and the organization continues to function efficiently.
In an age of shrinking margins, value-based care, and rising patient expectations, mastering RCM isn’t just an operational priority—it’s a strategic necessity. This guide dives deep into what RCM is, why it matters more than ever, and how healthcare providers can improve it in 2025 and beyond.
What is Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)?
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) refers to the financial process that healthcare providers use to track patient care episodes from registration and appointment scheduling to the final payment of a balance. It includes all administrative and clinical functions that contribute to the capture, management, and collection of patient service revenue.
Key Objectives of RCM:
-
Ensuring accurate patient data collection
-
Minimizing claim denials and delays
-
Reducing operational inefficiencies
-
Maximizing revenue generation
-
Maintaining compliance with regulations and payer policies
The Importance of RCM in Healthcare
With rising operational costs, strict regulations, and increasing patient volumes, healthcare providers must operate efficiently. A robust RCM system helps providers:
-
Enhance cash flow by speeding up billing and collections
-
Improve patient satisfaction through transparent billing processes
-
Ensure compliance with coding, documentation, and payer policies
-
Reduce errors in claims submission and payment processing
-
Boost operational efficiency and financial performance
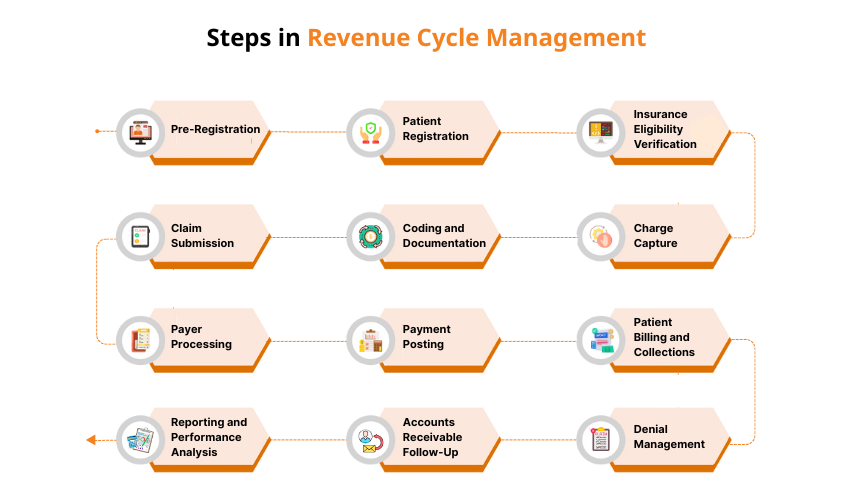
The Revenue Cycle: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is the process healthcare organizations use to track patient care episodes from registration to final payment. Each step plays a vital role in ensuring accurate billing, faster reimbursements, and a healthy cash flow. Below is a detailed look at each stage of the revenue cycle and how it contributes to financial success:
1. Pre-Registration
Before a patient arrives for their appointment, healthcare staff begin collecting essential information. This includes:
-
Basic demographics (name, date of birth, address)
-
Insurance provider and policy details
-
Reason for visit or scheduled procedure
Why it matters: Collecting this data early allows staff to verify insurance coverage and estimate patient costs, reducing future billing issues.
2. Patient Registration
During registration, patients provide or confirm their personal and insurance details. Front-office staff ensure the information is accurate and up to date.
Best practice: Use electronic forms and digital check-in systems to streamline the process and prevent manual entry errors.
3. Insurance Eligibility Verification
This step confirms whether the patient’s insurance is active and covers the planned services. It also checks for prior authorizations if required by the payer.
Why it’s crucial: Verifying eligibility prevents claim denials due to non-covered services or inactive policies, protecting your revenue from delays and write-offs.
4. Charge Capture
After the healthcare service is provided, all billable services are documented and translated into charge entries. This includes consultations, lab work, procedures, and more.
Goal: Ensure every service rendered is accurately recorded so no revenue is left on the table.
5. Medical Coding
Certified coders assign standardized codes (ICD, CPT, HCPCS) to diagnoses, procedures, and services. These codes form the foundation of the insurance claim.
Why coding accuracy matters: Correct coding ensures proper reimbursement and reduces the risk of audit penalties or denied claims.
6. Claim Creation and Submission
Once charges are captured and coded, the billing team compiles the information into an insurance claim. This claim is then submitted to the appropriate payer—either electronically or manually.
Tip: Use claims management software to automate claim scrubbing, reduce human error, and speed up submission timelines.
7. Payer Processing
Insurance companies review the submitted claims to determine if they meet the criteria for payment. The insurer will:
-
Approve and pay the claim
-
Partially pay the claim
-
Deny the claim and provide reasons
Key to success: Track claims closely and prepare for timely follow-ups on denials or requests for additional documentation.
8. Payment Posting
Once payments are received from insurers and patients, they are posted to the appropriate accounts in the billing system. Any adjustments, such as contractual allowances or patient balances, are also recorded.
Objective: Keep accurate financial records and reconcile accounts efficiently.
9. Patient Billing and Collections
If the insurance doesn’t cover the full cost, the remaining balance is billed to the patient. Clear communication about what is owed and how to pay is essential at this stage.
Best practice: Offer multiple payment methods and flexible plans to encourage faster payments and reduce accounts receivable.
10. Denial Management and Appeals
If a claim is denied, staff investigate the reason and take appropriate action—such as correcting errors or providing additional documentation—before resubmitting the claim.
Impact on revenue: Proactive denial management improves cash flow and reduces delays in revenue collection.
11. Accounts Receivable Follow-Up
For unpaid balances, follow-up communication with the patient or payer may be required. Collection efforts may involve reminders, calls, or working with third-party collection agencies.
Goal: Minimize bad debt and increase collections without compromising patient relationships.
12. Reporting and Performance Analysis
The final step involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as:
-
Days in Accounts Receivable (A/R)
-
Clean claim rate
-
Denial rate
-
Collection rate
Why it matters: Analyzing these metrics helps healthcare organizations identify areas for improvement, ensure compliance, and optimize the entire revenue cycle.
Best Practices for Effective Healthcare Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)
Implementing an effective Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) strategy requires accurate data collection, open patient communication, and continuous performance evaluation.
1. Comprehensive and Accurate Data Collection
At the very first point of contact, gather complete and accurate patient information. This includes:
-
Full name and contact details
-
Demographic data
-
Insurance provider and policy details
-
Health status and medical history
Use digital registration tools to streamline this process and ensure data is captured securely and accurately. Solid data collection at the front end reduces billing errors and insurance claim denials downstream.
2. Real-Time Insurance Verification
Verifying a patient’s insurance details before services are provided is essential. Implement real-time insurance verification tools to check:
-
Active coverage
-
Patient eligibility
-
Policy limits
-
Preauthorization requirements
Benefits: This minimizes claim rejections, clarifies financial responsibilities early on, and reduces surprise billing for patients.
3. Maintain Up-to-Date Patient Records
Ensure that patient records are continuously updated to reflect:
-
Changes in insurance
-
New contact information
-
Medical history updates
Educate patients on the importance of accurate and current information during the registration process. This ensures claims are submitted with correct, verified data and lowers the chances of processing delays.
4. Ensure Regulatory and Data Compliance
Design your registration and billing processes in accordance with:
-
HIPAA regulations
-
Data protection laws
-
Industry standards for electronic health information
Why it matters: Non-compliance can lead to audits, penalties, and lost revenue. A compliant process also builds patient trust.
5. Accurate Medical Coding
Medical coding is at the heart of claim accuracy and reimbursement. Invest in:
-
Ongoing training for coding staff
-
Regular updates on ICD-10 and CPT code changes
-
Coding audits to detect inconsistencies
Outcome: Proper coding reduces denials, maximizes reimbursements, and ensures regulatory compliance.
6. Automated Claim Scrubbing
Leverage automated claim scrubbing tools to detect and fix:
-
Missing fields
-
Invalid codes
-
Mismatched patient information
Scrubbed claims are more likely to be accepted on the first submission, leading to faster reimbursements and fewer rework cycles.
7. Efficient Claim Submission Process
Establish a clear, timely process for submitting claims to payers. Ensure that:
-
All required documentation is attached
-
Claims are complete and accurate
-
Submissions meet payer-specific requirements
Speed and accuracy in claim submission reduce accounts receivable days and improve cash flow.
8. Claim Tracking and Denial Management
Use tracking software to monitor each claim from submission through payment. For denied claims:
-
Respond quickly with corrected information
-
Track trends in denials (e.g., coding errors or missing authorizations)
-
Adjust internal processes to avoid repeat issues
Effective denial management is critical for revenue integrity and operational efficiency.
9. Transparent Patient Financial Communication
Proactively inform patients about:
-
Expected costs
-
Insurance coverage
-
Payment responsibilities
-
Billing timelines
Clear, upfront communication builds trust and increases the likelihood of timely payments.
10. Simplified Patient Invoicing
Make bills easy for patients to understand. Include:
-
Itemized charges
-
Insurance payments
-
Patient balance due
Offer multiple payment options such as online payments, credit/debit cards, digital wallets, and installment plans. Flexible payment options reduce bad debt and improve patient satisfaction.
11. Streamlined Payment Processing and Reconciliation
Create a structured process for:
-
Accepting patient payments
-
Posting payments to accounts promptly
-
Reconciling daily transactions
Integrated payment systems can automate these tasks, reducing errors and speeding up revenue collection.
12. Responsive Customer Service
Equip your billing and registration staff with:
-
Detailed knowledge of billing procedures
-
Training to explain insurance coverage and patient responsibilities
-
Tools to resolve billing inquiries quickly
A responsive and courteous customer service team enhances the patient financial experience, which is increasingly important in value-based care models.
13. Leverage RCM and Healthcare Technology
Adopt RCM software solutions and integrate them with your Electronic Health Record (EHR) system to:
-
Automate repetitive tasks
-
Reduce manual data entry errors
-
Get real-time analytics and reports
Advanced RCM technologies help accelerate collections, improve accuracy, and reduce administrative burden.
14. Monitor Key RCM Performance Metrics
Track and evaluate key Revenue Cycle Management KPIs, such as:
-
Days in A/R (Accounts Receivable)
-
Clean claim rate
-
First-pass resolution rate
-
Denial rate
-
Patient collection rate
Use these metrics to identify performance bottlenecks, evaluate staff efficiency, and guide improvement initiatives.
15. Continuously Improve Processes
RCM is not a set-it-and-forget-it function. Regularly review:
-
Internal workflows
-
Claims data
-
Patient feedback
-
Regulatory changes
Hold periodic performance reviews and strategy sessions to implement process improvements based on real data.
16. Invest in Staff Training
Ongoing training in areas like coding updates, compliance, and patient engagement is essential. Your RCM is only as strong as the people managing it.
17. Conduct Regular Audits
Audit both clinical and billing documentation to ensure accuracy and compliance. Identify patterns in denials and resolve root causes.
How Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) Impacts Healthcare Revenue
An effective Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) process directly influences a healthcare organization’s ability to collect timely and accurate payments. Each stage of the RCM cycle plays a crucial role in ensuring consistent cash flow and financial stability. Here’s how each component contributes to generating revenue:
1. Patient Registration
Accurate and complete collection of patient demographics, insurance details, and contact information during registration is the foundation of successful revenue generation. Proper patient data minimizes billing errors, reduces claim denials, and prevents delays in reimbursement.
2. Claim Creation and Submission
Generating clean claims with precise medical coding and documentation ensures that insurance providers can process them efficiently. Submitting claims on time increases the likelihood of faster payments and reduces administrative back-and-forth.
3. Payment Collection and Reconciliation
Tracking payments from both insurance companies and patients allows providers to quickly identify and resolve issues such as claim denials, underpayments, or outstanding balances. Effective collections management helps maintain a steady and predictable revenue stream.
4. Patient Financial Engagement
Proactive communication with patients about their financial responsibilities, billing questions, and available payment options improves transparency and builds trust. When patients understand their obligations, they are more likely to make timely payments, enhancing revenue flow.
5. Reporting and Financial Analytics
Analyzing RCM data provides valuable insights into payment trends, denial rates, and collection performance. These analytics empower decision-makers to optimize financial strategies, improve workflows, and increase overall revenue.
6. Regulatory and Payer Compliance
Staying compliant with changing healthcare regulations and insurance payer requirements is essential to avoid penalties or delays. A robust RCM process proactively manages compliance, reducing the risk of disruptions to revenue due to legal or audit issues.
How Technology Enhances Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare
Technology plays a transformative role in streamlining the revenue cycle management (RCM) process. By reducing manual work, minimizing errors, and accelerating payment cycles, healthcare providers can significantly improve their financial performance and operational efficiency. Here’s how modern digital tools and systems support and optimize each stage of RCM:
1. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) Integration
EHR systems centralize and integrate patient data across different care settings. This comprehensive access to real-time patient information improves clinical documentation and billing accuracy, ensuring that every service provided is correctly captured and billed. When RCM software integrates seamlessly with EHR systems, it reduces duplicate data entry, improves accuracy, and speeds up billing.
2. AI and Automation
-
Claim Scrubbing: Automated systems flag errors before submission.
-
Eligibility Verification: Bots can check insurance status instantly.
-
Denial Prediction: AI models predict which claims are at risk of being denied based on historical patterns.
3. Medical Coding Software
Advanced medical coding platforms—especially those powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning—help coding professionals assign accurate procedure and diagnosis codes. These tools reduce human error and ensure compliance with the latest coding standards, improving reimbursement rates.
4. Claims Management Systems
Claims management technology helps automate the creation, scrubbing, and submission of claims. These systems identify common errors, flag potential denials, and streamline the correction process—leading to faster payments and fewer rejections from insurers.
5. Electronic Billing and Payment Solutions
Digital billing platforms allow healthcare organizations to send patient invoices electronically and offer secure online payment options. This not only speeds up collections but also gives patients the convenience of paying bills through their preferred channels.
6. Healthcare Data Analytics and Reporting Tools
Sophisticated analytics solutions provide in-depth insights into financial performance, denial trends, and operational bottlenecks. With these tools, healthcare administrators can make data-driven decisions to optimize revenue cycles and improve long-term financial health.
7. Patient Financial Engagement Platforms
Patient portals and engagement tools improve communication regarding financial obligations. These platforms allow patients to view bills, explore payment plans, make online payments, and access helpful resources—resulting in better payment compliance and patient satisfaction.
8. Denial Management Technology
Dedicated software for denial tracking and analysis helps providers understand why claims are being rejected. These tools identify recurring denial patterns, enabling organizations to take corrective action and reduce future occurrences.
9. Automation of Administrative Tasks
Automation reduces the burden on administrative staff by handling routine processes such as appointment reminders, insurance checks, and payment follow-ups. This improves staff productivity and allows teams to focus on more strategic RCM activities.
10. Data Analytics and Dashboards
Advanced analytics give providers real-time insights into KPIs like denial rates, days in A/R, and collection efficiency. This empowers better decision-making.
Common RCM Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Despite its importance, RCM is prone to multiple challenges that can hinder financial performance.
1. Claim Denials
Claim denials are one of the most common and costly problems. Denials occur due to errors in coding, documentation, or eligibility verification.
Solutions:
-
Implement denial management workflows
-
Conduct root cause analysis
-
Train staff regularly
2. Regulatory Compliance
Staying compliant with HIPAA, CMS, and payer-specific rules requires constant vigilance.
Solutions:
-
Use compliance management software
-
Regularly update staff on policy changes
-
Conduct audits and risk assessments
3. Patient Payment Collections
With the rise of high-deductible health plans, patients are now responsible for a larger portion of healthcare costs. Collecting these payments can be difficult.
Solutions:
-
Provide transparent pricing upfront
-
Offer flexible payment plans
-
Use patient-friendly billing tools
4. Data Silos and Inefficient Workflows
Lack of integration between EHRs, billing systems, and payer portals can cause data silos, leading to inefficiencies and errors.
Solutions:
-
Invest in interoperable systems
-
Use centralized dashboards
-
Automate repetitive tasks
5. Staffing Shortages
RCM requires skilled professionals in billing, coding, and compliance. Staffing shortages can delay revenue recovery.
Solutions:
-
Outsource to specialized RCM firms
-
Provide ongoing training and development
-
Leverage AI and automation
RCM Technology Trends in 2025
The future of RCM lies in automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics. Let’s explore emerging technologies transforming RCM.
1. AI-Powered Coding and Billing
AI can automate complex coding tasks, detect documentation gaps, and suggest correct codes, reducing human error and boosting efficiency.
2. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA is being used to streamline repetitive tasks such as claim status checks, payment posting, and denial management.
3. Predictive Analytics
By analyzing past data, predictive tools can forecast cash flow, identify high-risk claims, and suggest proactive solutions.
4. Integrated Patient Portals
Modern RCM platforms include patient-facing features such as:
-
Real-time insurance verification
-
Digital statements
-
Online payment options
5. Blockchain for Healthcare Payments
Blockchain can offer secure, transparent, and real-time verification of healthcare transactions, helping eliminate fraud and disputes.
In-House vs. Outsourced RCM: What’s Better?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer, but here’s a quick comparison to help you decide:
| Factor | In-House RCM | Outsourced RCM |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Full control over operations | Less control, more reliance on vendor |
| Cost | Higher fixed costs (salaries, tools) | Variable cost, based on volume or % collected |
| Expertise | Needs internal expertise | Access to billing and compliance specialists |
| Scalability | May require hiring and training | Scales easily with volume |
Pro tip: Hybrid models (outsourcing specific functions like denial management) are becoming more common.
Conclusion: RCM Is No Longer Just a Back-Office Task
Revenue Cycle Management is now a strategic pillar in healthcare. From improving cash flow and ensuring compliance to enhancing the patient experience, RCM plays a central role in keeping modern healthcare systems viable.
Whether you’re running a small private practice or a multi-site health system, it’s time to rethink RCM as a dynamic, tech-driven, patient-first operation. The right tools, processes, and people can make your revenue cycle not just efficient—but exceptional.